Chemistry:Methanediol
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methanediol[1] | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | MADOL | ||
| 1730798 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 48.041 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Boiling point | 194 °C (381 °F; 467 K) at 101 kPa [citation needed] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 16.1 Pa [citation needed] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.29[2] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.401 [citation needed] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 99.753 °C (211.555 °F; 372.903 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
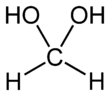
Methanediol, also known as formaldehyde monohydrate or methylene glycol, is an organic compound with chemical formula CH
2(OH)
2. It is the simplest geminal diol. In aqueous solutions it coexists with oligomers (short polymers). The compound is closely related and convertible to the industrially significant derivatives paraformaldehyde ((CH
2O)
n), formaldehyde (H
2C=O), and 1,3,5-trioxane ((CH
2O)
3).[3]
Methanediol is a product of the hydration of formaldehyde. The equilibrium constant for hydration is estimated to be 103,[4]CH
2(OH)
2 predominates in dilute (<0.1%) solution. In more concentrated solutions, it oligomerizes to HO(CH
2O)
nH.[3]
Occurrence
The dianion, methanediolate, is believed to be an intermediate in the crossed Cannizzaro reaction.
Gaseous methanediols can be generated by electron irradiation and sublimation of a mixture of methanol and oxygen ices.[5]
Methanediol is believed to occur as an intermediate in the decomposition of carbonyl compounds in the atmosphere, and as a product of ozonolysis on these compounds.[5]
Safety
Methanediol, rather than formaldehyde, is listed as one of the main ingredients of "Brazilian blowout", a hair-straightening formula marketed in the United States . The equilibrium with formaldehyde has caused concern since formaldehyde in hair straighteners is a health hazard.[6][7] Research funded by the Professional Keratin Smoothing Council (PKSC), an industry association that represents selected manufacturers of professional-use only keratin smoothing products, has disputed the risk.[8]
See also
- Orthoformic acid (methanetriol)
- Orthocarbonic acid (methanetetrol)
References
- ↑ "Methanediol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=79015. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
- ↑ Bell, R. P.; McTigue, P. T. (1960). "603. Kinetics of the aldol condensation of acetaldehyde". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 2983. doi:10.1039/JR9600002983.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Reuss, Günther; Disteldorf, Walter; Gamer, Armin Otto; Hilt, Albrecht (2000). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_619.
- ↑ Eric V. Anslyn, Dennis A. Dougherty (2006), Modern physical organic chemistry. University Science Books. ISBN 1-891389-31-9. 1095 pages
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Zhu, Cheng; Kleimeier, N. Fabian; Turner, Andrew M.; Singh, Santosh K.; Fortenberry, Ryan C.; Kaiser, Ralf I. (4 January 2022). "Synthesis of methanediol [CH 2 (OH) 2 : The simplest geminal diol"]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 119 (1): e2111938119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2111938119. PMID 34969838. Bibcode: 2022PNAS..11911938Z.
- ↑ "Hair Smoothing Products That Could Release Formaldehyde". Occupational Safety and Health Administration. https://www.osha.gov/SLTC/formaldehyde/hazard_alert.html.
- ↑ SpecialChem. "Industry News". http://www.specialchem4cosmetics.com/markets/hair-care/news.aspx?id=5947&lr=chal2d161210&li=100091733.
- ↑ Golden, R.; Valentini, M. (July 2014). "Formaldehyde and methylene glycol equivalence: Critical assessment of chemical and toxicological aspects". Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 69 (2): 178–186. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.03.007. PMID 24709515.
 |