Chemistry:Oxetacaine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
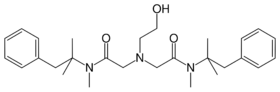 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 1 hour |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H41N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 467.654 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Oxetacaine (INN, also known as oxethazaine) is a potent local anesthetic. It is administered orally (usually in combination with an antacid) for the relief of pain associated with peptic ulcer disease or esophagitis. One example of such a product is Mucaine Gel, indicated for "rapid and effective relief in gastritis, esophagitis, hiatus hernia, heartburn of pregnancy and peptic ulcer".[1] It is also used topically in the management of hemorrhoid pain. Oral oxetacaine preparations are available in several countries, including India , South Africa , Japan , Taiwan and Brazil , but not the United States. Unlike most local anesthetics, oxetacaine does not break down under strongly acidic conditions.[2]
References
- ↑ "Mucaine Gel". Pfizer. https://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=14808.
- ↑ "Oxethazaine and related congeners: a series of highly potent local anesthetics". Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 109 (3): 664–8. 1962. doi:10.3181/00379727-109-27300. PMID 13910333.
External links
- Strocain Prescribing information from Eisai Co.
 |
