Chemistry:Zirconium nitride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Zirconium nitride
| |
| Other names
Zirconium(III) nitride, Nitridozirconium
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| ZrN[1] | |
| Appearance | Yellow-brown crystals |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 7.09 g/cm3 (24 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 2,952 °C (5,346 °F; 3,225 K) at 760 mmHg[1] |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | Soluble in concentrated HF, acids[1] |
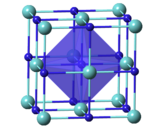
| Structure | |
| Cubic, cF8[2] | |
| Fm3m, No. 225[2] | |
a = 4.5675 Å[2] α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 90°
| |
| Octahedral[2] | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
40.442 J/mol·K[3] |
Std molar
entropy (S |
38.83 J/mol·K[3] |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−365.26 kJ/mol[3] |
| Related compounds | |
Related refractory ceramic materials
|
Tantalum carbide Niobium carbide Zirconium carbide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Zirconium nitride (ZrN) is an inorganic compound used in a variety of ways due to its properties.
Properties
ZrN grown by physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a light gold color similar to elemental gold. ZrN has a room-temperature electrical resistivity of 12.0 µΩ·cm, a temperature coefficient of resistivity of 5.6·10−8 Ω·cm/K, a superconducting transition temperature of 10.4 K, and a relaxed lattice parameter of 0.4575 nm. The hardness of single-crystal ZrN is 22.7±1.7 GPa and elastic modulus is 450 GPa.[4]
Uses

Zirconium nitride is a hard ceramic material similar to titanium nitride and is a cement-like refractory material. Thus it is used in cermets and laboratory crucibles. When applied using the physical vapor deposition coating process it is commonly used for coating medical devices,[5] industrial parts (notably drill bits), automotive and aerospace components and other parts subject to high wear and corrosive environments.
Zirconium nitride was suggested as a hydrogen peroxide fuel tank liner for rockets and aircraft.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Lide, David R., ed (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Sirajuddeen, M. Md. Sheik.; Banu, I. B. S. (2014). "FP-LAPW investigation of electronic, magnetic, elastic and thermal properties of Fe-doped zirconium nitride". AIP Advances 4 (5): 057121. doi:10.1063/1.4879798. Bibcode: 2014AIPA....4e7121S.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Zirconium nitride in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD), http://webbook.nist.gov (retrieved 2014-06-30)
- ↑ Mei, A. B.; Howe, B. M.; Zhang, C.; Sardela, M.; Eckstein, J. N.; Hultman, L.; Rockett, A.; Petrov, I. et al. (2013). "Physical properties of epitaxial ZrN/MgO(001) layers grown by reactive magnetron sputtering". Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films 31 (6): 061516. doi:10.1116/1.4825349. Bibcode: 2013JVSTA..31f1516M.
- ↑ "Slate, A.J., Wickens, D.J., El Mohtadi, M. et al. Antimicrobial activity of Ti-ZrN/Ag coatings for use in biomaterial applications. Sci Rep 8, 1497 (2018)". https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20013-z.
- ↑ Yousefiani, Ali, "Coating for components requiring hydrogen peroxide compatibility", US patent 7736751, published 2010-06-15
| NH3 | He(N2)11 | ||||||||||||||||
| Li3N | Be3N2 | BN | β-C3N4 g-C3N4 |
N2 | NxOy | NF3 | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na3N | Mg3N2 | AlN | Si3N4 | PN P3N5 |
SxNy SN S4N4 |
NCl3 | Ar | ||||||||||
| K3N | Ca3N2 | ScN | TiN | VN | CrN Cr2N |
MnxNy | FexNy | CoN | Ni3N | CuN | Zn3N2 | GaN | Ge3N4 | As | Se | NBr3 | Kr |
| Rb3N | Sr3N2 | YN | ZrN | NbN | β-Mo2N | Tc | Ru | Rh | PdN | Ag3N | CdN | InN | Sn | Sb | Te | NI3 | Xe |
| Cs3N | Ba3N2 | Hf3N4 | TaN | WN | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg3N2 | TlN | Pb | BiN | Po | At | Rn | |
| Fr3N | Ra3N | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | CeN | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | GdN | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UN | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

