Chemistry:Sodium nitride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium nitride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| EC Number |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Na3N | |
| Molar mass | 82.976 g/mol |
| Appearance | reddish brown or dark blue solid |
| Melting point | 87 °C (189 °F; 360 K)[1] (decomposes) |
| reacts | |
| Structure | |
| Cubic, cP4[2] | |
| Pm3m[2] | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-151 J/mol[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Sodium amide Sodium imide |
Other cations
|
Lithium nitride Potassium nitride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sodium nitride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na3N. In contrast to lithium nitride and some other nitrides, sodium nitride is an extremely unstable alkali metal nitride. It can be generated by combining atomic beams of sodium and nitrogen deposited onto a low-temperature sapphire substrate.[1] It readily decomposes into its elements:
- [math]\ce{ 2 Na3N -> 6 Na + N2 }[/math]
Synthesis
Sodium nitride can be synthesized in two different ways: by the thermal decomposition of NaNH2 or by the direct reaction of the elements.[2] The most common way to successfully synthesize sodium nitride has been done by Dieter Fischer & Martin Jansen and Grigori Vajenine using the latter method. The first way is to introduce desired ratios of Na and N2 in gas phase separately and depositing them in a vacuum chamber on a cooled substrate, which is then heated to room temperate (298 K) to crystallize.[1] The second method is to react elemental sodium with plasma activated nitrogen on a metal surface. This synthesis can be further facilitated by introducing liquid Na-K alloy to the compound with the excess liquid removed and washed with fresh alloy. The solid is then separated from the liquid using a centrifuge. However Vajenine’s method is very air-sensitive and can decompose and combust rapidly, unless exposed to a pure oxygen (O2) environment.[3]
Characteristics
Sodium nitride can be of reddish brown or dark blue color depending on the synthesis of the compound due to intrinsic properties.[1][3] It shows no signs of decomposition after several weeks when at room temperature.[3] The compound does not have a melting point as it decomposes back into its elemental forms as demonstrated using mass spectrometry around 360 K.[1][2] The estimated enthalpy of formation for the compound is +64 kJ/mol.[3]
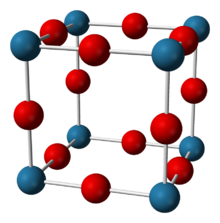
Structure
Sodium nitride seems to be about 90% ionic at room temperature, but has the band gap typical for a semiconductor.[2][3] It adopts the anti-ReO3 structure with a simple lattice made up of NNa6 octahedra.[1][2][3][4] The compound has N−Na bond lengths of 236.6 pm.[1][3] This structure has been confirmed through X-ray diffraction and more recently neutron diffraction on powder and single crystals.[1][2][3][4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Fischer, D., Jansen, M. (2002). "Synthesis and structure of Na3N". Angew Chem 41 (10): 1755–1756. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20020517)41:10<1755::AID-ANIE1755>3.0.CO;2-C. PMID 19750706. Fischer, D.; Cancarevic, Z.; Schön, J. C.; Jansen, M. Z. (2004). "Synthesis and structure of K3N". Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 630 (1): 156. doi:10.1002/zaac.200300280.. 'Elusive Binary Compound Prepared' Chemical & Engineering News 80 No. 20 (20 May 2002)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Sangster, J. (2004). "N-Na(Nitrogen-Sodium) System". Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion 25 (6): 560–563. doi:10.1007/s11669-004-0082-0.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Vajenine, G.V. (2007). "Plasma-Assisted Synthesis and Properties of Na3N". Inorganic Chemistry 46 (13): 5146–5148. doi:10.1021/ic700406q. PMID 17530752.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Vajenine, G. V., Hoch, C., Dinnebier, R. E., Senyshyn, A., Niewa, R. (2009). "A Temperature-dependent Structural Study of anti-ReO3-type Na3N: to Distort or not to Distort?". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 636 (1): 94–99. doi:10.1002/zaac.200900488.
| NH3 | He(N2)11 | ||||||||||||||||
| Li3N | Be3N2 | BN | β-C3N4 g-C3N4 |
N2 | NxOy | NF3 | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na3N | Mg3N2 | AlN | Si3N4 | PN P3N5 |
SxNy SN S4N4 |
NCl3 | Ar | ||||||||||
| K3N | Ca3N2 | ScN | TiN | VN | CrN Cr2N |
MnxNy | FexNy | CoN | Ni3N | CuN | Zn3N2 | GaN | Ge3N4 | As | Se | NBr3 | Kr |
| Rb3N | Sr3N2 | YN | ZrN | NbN | β-Mo2N | Tc | Ru | Rh | PdN | Ag3N | CdN | InN | Sn | Sb | Te | NI3 | Xe |
| Cs3N | Ba3N2 | Hf3N4 | TaN | WN | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg3N2 | TlN | Pb | BiN | Po | At | Rn | |
| Fr3N | Ra3N | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | CeN | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | GdN | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UN | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

