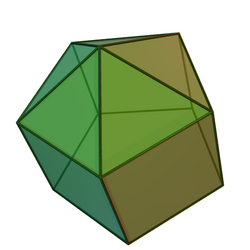
Elongated pentagonal pyramid
| Elongated pentagonal pyramid | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Johnson J8 – J9 – J10 |
| Faces | 5 triangles 5 squares 1 pentagon |
| Edges | 20 |
| Vertices | 11 |
| Vertex configuration | 5(42.5) 5(32.42) 1(35) |
| Symmetry group | C5v, [5], (*55) |
| Rotation group | C5, [5]+, (55) |
| Dual polyhedron | self-dual[1] |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
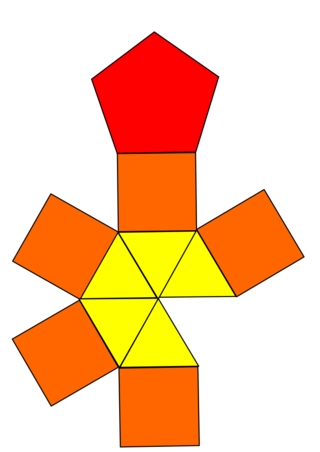 | |
File:J9 elongated pentagonal pyramid.stl The elongated pentagonal pyramid is a polyhedron constructed by attaching one pentagonal pyramid onto one of the pentagonal prism's bases, a process known as elongation. It is an example of composite polyhedron.[2][3] This construction involves the removal of one pentagonal face and replacing it with the pyramid. The resulting polyhedron has five equilateral triangles, five squares, and one pentagon as its faces.[4] It remains convex, with the faces are all regular polygons, so the elongated pentagonal pyramid is Johnson solid, enumerated as the ninth Johnson solid .[5]
For edge length , an elongated pentagonal pyramid has a surface area by summing the area of all faces, and volume by totaling the volume of a pentagonal pyramid's Johnson solid and regular pentagonal prism:[4]
The elongated pentagonal pyramid has a dihedral between its adjacent faces:[6]
- the dihedral angle between adjacent squares is the internal angle of the prism's pentagonal base, 108°;
- the dihedral angle between the pentagon and a square is the right angle, 90°;
- the dihedral angle between adjacent triangles is that of a regular icosahedron, 138.19°; and
- the dihedral angle between a triangle and an adjacent square is the sum of the angle between those in a pentagonal pyramid and the angle between the base of and the lateral face of a prism, 127.37°.
References
- ↑ Draghicescu, Mircea. "Dual Models: One Shape to Make Them All". Bridges Finland: Mathematics, Music, Art, Architecture, Education, Culture. pp. 635–640. https://archive.bridgesmathart.org/2016/bridges2016.
- ↑ Timofeenko, A. V. (2010). "Junction of Non-composite Polyhedra". St. Petersburg Mathematical Journal 21 (3): 483–512. doi:10.1090/S1061-0022-10-01105-2. https://www.ams.org/journals/spmj/2010-21-03/S1061-0022-10-01105-2/S1061-0022-10-01105-2.pdf.
- ↑ Rajwade, A. R. (2001). Convex Polyhedra with Regularity Conditions and Hilbert's Third Problem. Texts and Readings in Mathematics. Hindustan Book Agency. p. 84–89. doi:10.1007/978-93-86279-06-4. ISBN 978-93-86279-06-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=afJdDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA84.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Berman, Martin (1971). "Regular-faced convex polyhedra". Journal of the Franklin Institute 291 (5): 329–352. doi:10.1016/0016-0032(71)90071-8.
- ↑ Uehara, Ryuhei (2020). Introduction to Computational Origami: The World of New Computational Geometry. Springer. p. 62. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-4470-5. ISBN 978-981-15-4470-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=51juDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA62.
- ↑ "Convex polyhedra with regular faces". Canadian Journal of Mathematics 18: 169–200. 1966. doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8.
External links
 |
