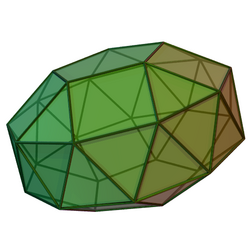
Gyroelongated pentagonal bicupola
| Gyroelongated pentagonal bicupola | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Johnson J45 – J46 – J47 |
| Faces | 3.10 triangles 10 squares 2 pentagons |
| Edges | 70 |
| Vertices | 30 |
| Vertex configuration | 10(3.4.5.4) 2.10(34.4) |
| Symmetry group | D5 |
| Dual polyhedron | - |
| Properties | convex, chiral |
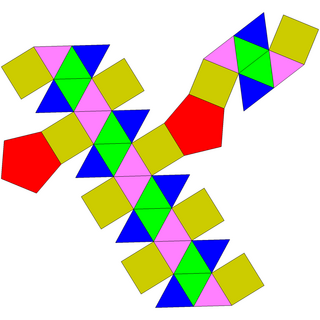
| Net | |
 | |
In geometry, the gyroelongated pentagonal bicupola is one of the Johnson solids (J46). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by gyroelongating a pentagonal bicupola (J30 or J31) by inserting a decagonal antiprism between its congruent halves.
The gyroelongated pentagonal bicupola is one of five Johnson solids which are chiral, meaning that they have a "left-handed" and a "right-handed" form. In the illustration to the right, each square face on the bottom half of the figure is connected by a path of two triangular faces to a square face above it and to the right. In the figure of opposite chirality (the mirror image of the illustrated figure), each bottom square would be connected to a square face above it and to the left. The two chiral forms of J46 are not considered different Johnson solids.
A Johnson solid is one of 92 strictly convex polyhedra that is composed of regular polygon faces but are not uniform polyhedra (that is, they are not Platonic solids, Archimedean solids, prisms, or antiprisms). They were named by Norman Johnson, who first listed these polyhedra in 1966.[1]
Area and Volume
With edge length a, the surface area is
- [math]\displaystyle{ A=\frac{1}{2}\left(20+15\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{25+10\sqrt{5}}\right)a^2\approx26.431335858...a^2, }[/math]
and the volume is
- [math]\displaystyle{ V=\left(\frac{5}{3}+\frac{4}{3}\sqrt{5} + \frac{5}{6}\sqrt{2\sqrt{650+290\sqrt{5}}-2\sqrt{5}-2}\right) a^3\approx11.397378512...a^3. }[/math]
External links
 |
- ↑ Johnson, Norman W. (1966), "Convex polyhedra with regular faces", Canadian Journal of Mathematics 18: 169–200, doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8.

