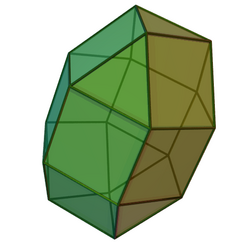
Elongated triangular gyrobicupola
| Elongated triangular gyrobicupola | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Johnson J35 – J36 – J37 |
| Faces | 8 triangles 12 squares |
| Edges | 36 |
| Vertices | 18 |
| Vertex configuration | |
| Symmetry group | |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |
In geometry, the elongated triangular gyrobicupola is a polyhedron constructed by attaching two regular triangular cupolas to the base of a regular hexagonal prism, with one of them rotated in . It is an example of Johnson solid.
Construction
The elongated triangular gyrobicupola is similarly can be constructed as the elongated triangular orthobicupola, started from a hexagonal prism by attaching two regular triangular cupolae onto its base, covering its hexagonal faces.[1] This construction process is known as elongation, giving the resulting polyhedron has 8 equilateral triangles and 12 squares.[2] The difference between those two polyhedrons is one of two triangular cupolas in the elongated triangular gyrobicupola is rotated in . A convex polyhedron in which all faces are regular is Johnson solid, and the elongated triangular gyrobicupola is one among them, enumerated as 36th Johnson solid .[3]
Properties
An elongated triangular gyrobicupola with a given edge length has a surface area by adding the area of all regular faces:[2] Its volume can be calculated by cutting it off into two triangular cupolae and a hexagonal prism with regular faces, and then adding their volumes up:[2]
Its three-dimensional symmetry groups is the prismatic symmetry, the dihedral group of order 12.[clarification needed] Its dihedral angle can be calculated by adding the angle of the triangular cupola and hexagonal prism. The dihedral angle of a hexagonal prism between two adjacent squares is the internal angle of a regular hexagon , and that between its base and square face is . The dihedral angle of a regular triangular cupola between each triangle and the hexagon is approximately , that between each square and the hexagon is , and that between square and triangle is . The dihedral angle of an elongated triangular orthobicupola between the triangle-to-square and square-to-square, on the edge where the triangular cupola and the prism is attached, is respectively:[4]
Related polyhedra and honeycombs
The elongated triangular gyrobicupola forms space-filling honeycombs with tetrahedra and square pyramids.[5]
References
- ↑ Rajwade, A. R. (2001). Convex Polyhedra with Regularity Conditions and Hilbert's Third Problem. Texts and Readings in Mathematics. Hindustan Book Agency. p. 84–89. doi:10.1007/978-93-86279-06-4. ISBN 978-93-86279-06-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=afJdDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA84.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Berman, Martin (1971). "Regular-faced convex polyhedra". Journal of the Franklin Institute 291 (5): 329–352. doi:10.1016/0016-0032(71)90071-8.
- ↑ Francis, Darryl (August 2013). "Johnson solids & their acronyms". Word Ways 46 (3): 177. https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA340298118.
- ↑ "Convex polyhedra with regular faces". Canadian Journal of Mathematics 18: 169–200. 1966. doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8.
- ↑ "J36 honeycomb". http://woodenpolyhedra.web.fc2.com/J36.html.
External links
 |
