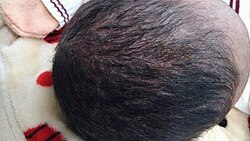
Medicine:Seborrhoeic dermatitis
| Seborrhoeic dermatitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Sebopsoriasis, seborrhoeic eczema, pityriasis capitis[1] |
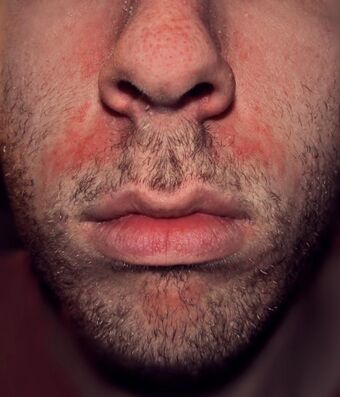 | |
| Seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Flaking, dry or greasy, red, itchy, and inflamed skin[2][3] |
| Duration | Several weeks to lifelong [4] |
| Causes | Multiple factors[4] |
| Risk factors | Stress, dry skin, winter, poor immune function, Parkinson disease[4] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms[4] |
| Differential diagnosis | Psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, tinea capitis, rosacea, systemic lupus erythematosus[4] |
| Treatment | Humidifier |
| Medication | Antifungal cream, anti-inflammatory agents, coal tar, phototherapy[3] |
| Frequency | ~5% (adults),[4] ~10% (babies)[5] |
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is a long-term skin disorder.[4] Symptoms include flaky, scaly, greasy, and occasionally itchy and inflamed skin.[2][3] Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest.[4] It can result in social or self-esteem problems.[4] In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap.[2] Seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp may be described in lay terms as dandruff due to the dry, flaky character of the skin.[6] However, as dandruff may refer to any dryness or scaling of the scalp, not all dandruff is seborrhoeic dermatitis.[6] Seborrhoeic dermatitis is sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea.[4]
The cause is unclear but believed to involve a number of genetic and environmental factors.[2][4] Risk factors for seborrhoeic dermatitis include poor immune function, Parkinson's disease, and alcoholic pancreatitis.[4][6] The condition may worsen with stress or during the winter.[4] Malassezia yeast is believed to play a role.[6] It is not a result of poor hygiene.[7] Diagnosis is typically clinical and based on the symptoms present.[4][8] The condition is not contagious.[9]
The typical treatment is topical antifungal cream and anti-inflammatory agents.[3] Specifically, ketoconazole or ciclopirox are effective.[10] Seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp is often treated with shampoo preparations of ketoconazole or zinc pyrithione.[11]
The condition is common in infants within the first three months of age or in adults aged 30 to 70 years.[2][4][5] It tends to affect more males.[12] Seborrhoeic dermatitis is more common in African Americans, among individuals who are immune compromised, such as with HIV, and individuals with Parkinson's disease.[11][12]
Signs and symptoms
Seborrhoeic dermatitis typically appears as dry, white, flaky skin. The flakes can be fine, loose, and diffuse or thick and adherent.[11][8] Additionally, flakes can appear yellow and oily or greasy.[8][12] In addition to flaky skin, seborrhoeic dermatitis can have areas of red, inflamed, and itchy skin that coincide with the area of skin flaking, but not all individuals have this symptom.[8] seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp can appear similarly to dandruff.[11] When the scalp is affected, there can be associated temporary hair loss.[11] Such hair loss varies in appearance from diffuse thinning to patchy areas of hair loss.[11] On close inspection, the locations where hair has thinned may have broken stubs of hair and pustules around the hair follicles.[11] Individuals with more pigmented skin tones may experience increased or decreased skin pigmentation in affected areas.[12]
Various locations can be affected by seborrhoeic dermatitis. Commonly affected areas include the face, ears, scalp, and across the body. It is less common in intertriginous areas, which are areas where the skin folds and comes into contact with itself, such as the groin or underarm.[11]
Seborrhoeic dermatitis' symptoms are typically mild and appear gradually but are often persistent, lasting weeks to years.[8][11][13] Individuals with seborrhoeic dermatitis are subject to recurrent bouts and it may be a lifelong condition.[8] Seborrhoeic dermatitis can also occur quickly and severely in patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). In fact, this is sometimes the first indication of HIV.[12]
Causes
The cause of seborrhoeic dermatitis has not been fully clarified.[1][14]
In addition to the presence of Malassezia, genetic, environmental, hormonal, and immune-system factors are necessary for and/or modulate the expression of seborrhoeic dermatitis.[15][16] The condition may be aggravated by illness, psychological stress, fatigue, sleep deprivation, change of season, and reduced general health.[17]
Fungi
The condition is thought to be due to a local inflammatory response to overgrowth by Malassezia fungi species in sebum-producing skin areas including the scalp, face, chest, back, underarms, and groin.[3][14] This is based on observations of high counts of Malassezia species in skin affected by seborrhoeic dermatitis and on the effectiveness of antifungals in treating the condition.[14] Species of Malassezia implicated in Seborrhoeic dermatitis include M. furfur (formerly Pityrosporum ovale), M. globosa, M. restricta, M. sympodialis, and M. slooffiae.[3] Malassezia appears to be the significant factor in seborrhoeic dermatitis but it is thought that other factors are necessary for the presence of Malassezia to result in the seborrhoeic dermatitis.[14] For example, summer growth of Malassezia in the skin alone does not result in seborrhoeic dermatitis.[14] Besides antifungals, the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory drugs, which reduce inflammation, and antiandrogens, which reduce sebum production, provide further insights into the pathophysiology of seborrhoeic dermatitis.[3][18][19]
Bacteria
Several bacteria, including Propionibacterium species and Staphylococcus aureus, have been shown to have some level of interaction with seborrhoeic dermatitis, though their exact impact is not known.[20][12]
Nutrition
Seborrhoeic dermatitis-like eruptions are also associated with pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and riboflavin (vitamin B2) deficiency.[21][8] In children and babies, issues with Δ6-desaturase enzymes[17] have been correlated with increased risk.
Immune dysfunction
Those with immunodeficiency (especially infection with HIV) and with neurological disorders that may impact immune system function such as Parkinson's disease (for which the condition is an autonomic sign) and stroke are particularly prone to it.[22]
Climate
Climate can affect seborrheic dermatitis, but there is a lack of consensus about which climates tend to exacerbate seborrheic dermatitis the most. Some studies show low humidity and low temperature are responsible for high frequency of seborrheic dermatitis.[23] Others suggest hot environments may also worsen seborrhoeic dermatitis.[12] Yet another described that high humidity and low UV exposure are culpable.[24] Dry skin and an impaired skin barrier contribute to the condition.[12][20] It is likely that climate and weather variations affect the water and lipid content of skin.[20]
Mechanism
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is a complex condition with many interacting factors that are not yet fully explained.[14] In general, the major factors that influence the development and severity include Malassezia yeast presents on and in the skin, skin production of oily sebum, and a subsequent inflammatory response against Malassezia and their byproducts.[12] Additional factors involved in the condition are a compromised skin barrier, the makeup and amount of sebum produced, the character of the immune response and inflammation, and the presence of other microbes species inhabiting the skin.[14][12] A suggested series of events leading to seborrhoeic dermatitis are initial damaged skin barrier and abnormal sebum production which leads to a change in the microbiome of the skin that in turn elicits an immune response.[14] An alternative explanation is an increase in sebum production feeding an increase in the Malassezia population that instigates inflammation; the inflammation then causes cellular changes that damage the skin barrier. This barrier disruption then encourages additional Malassezia growth and inflammation and again worsened skin barrier function.[12]
Diagnosis
Typically, seborrhoeic dermatitis is a clinical diagnosis based off a physician's expertise in identifying and differentiating skin conditions based on the history of the individual and the appearance of the skin.[8] However, seborrhoeic dermatitis may also be diagnosed with additional testing. The least invasive test is a visual inspection in the clinic using a Wood's Lamp.[11] A KOH test can also be used, where skin scraping of the affected skin may also be taken and prepared with potassium hydroxide (KOH) and visualized under a microscope to look for Malassezia or other microbiological cell. Additionally, a fungal culture of the affected skin may be taken to attempt to grow and identify the causative organism.[11]
Differential diagnosis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis can look similar to other skin conditions that share its characteristic dry, flaky, scaly, and inflamed appearance but have different causes and treatments. Physicians use the history of the individual with the skin condition as well as other tests to identify which disorder is present. Other conditions that may be confused with seborrhoeic dermatitis based on appearance are listed below.[8][11]
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema)[11]
- Contact dermatitis[8]
- Psoriasis[11]
- Tinea capitis and tinea corporis[8]
- Candidiasis[12]
- Tinea versicolor[8]
- Pityriasis rosea[8]
- Impetigo[12]
- Drug reaction[12]
- Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma[11]
Management
Medications
A variety of different types of medications are able to reduce symptoms of seborrhoeic dermatitis.[3] These include certain antifungals, anti-inflammatory agents like corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiandrogens, and antihistamines, among others.[3][1] Treatments must take into consideration potential side effects, especially with long-term use given the chronic nature of seborrhoeic dermatitis. Initial therapy is usually a topical preparation with an agreeable side effect profile.[12]
Antifungals
Regular use of an over-the-counter or prescription antifungal shampoo or cream is a common treatment. The topical antifungal medications ketoconazole and ciclopirox have the best evidence.[10] Ketoconazole should be used twice per week.[8] Shampoo or soap containing zinc pyrithione or selenium sulfide is also used.[8] These options should be used on a daily basis but may also be used in conjunction with a ketoconazole shampoo regimen on alternate days.[8] It is unclear if other antifungals are equally effective as this has not been sufficiently studied.[10] Antifungals that have been studied and found to be effective in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis include ketoconazole, fluconazole, miconazole, bifonazole, sertaconazole, clotrimazole, flutrimazole, ciclopirox, terbinafine, butenafine, selenium disulfide, and lithium salts such as lithium gluconate and lithium succinate.[10][3] Topical climbazole appears to have little effectiveness in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis.[10] Systemic therapy with oral antifungals including itraconazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole is effective, but adverse side effects have been documented for fluconazole and ketoconazole, with the latter not recommended for use, while itraconazole, with its good safety profile, is the most commonly prescribed.[3] Terbinafine is said to be effective, but with adverse side effects, while other sources state it is not effective and should not be used.[3][11]
Anti-inflammatory treatments
Topical corticosteroids have been shown to be effective in short-term treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis. They cannot be used long term or for maintenance because of their skin-thinning side effect. Accordingly, these are used for only a few weeks at a time.[11] There is also evidence for the effectiveness of topical calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus as well as lithium salt therapy.[25] Calcineurin inhibitors were also effective in reducing growth of Malassezia, offering two routes by which they may treat seborrhoeic dermatitis.[24] Medications such as the calcineurin inhibitors should not be used in individuals with seborrhoeic dermatitis who are immune compromised because they cause further immune suppression.[11]
Oral immunosuppressive treatment, such as with prednisone, has been used in short courses for seborrhoeic dermatitis, as a last resort due to its potential side effects.[26]
Antiandrogens
Seborrhoea, which is sometimes associated with seborrhoeic dermatitis,[27][28][29] is recognized as an androgen-sensitive condition – that is, it is caused or aggravated by androgen sex hormones such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone – and is a common symptom of hyperandrogenism (e.g., that seen in polycystic ovary syndrome).[30][31] In addition, seborrhoeic dermatitis, as well as acne, are commonly associated with puberty due to the steep increase of androgen levels at that time.[32] Males have increased activity of sebacious glands and are more likely to have seborrhoeic dermatitis.[20] Skin with increased sebacious glands is also more likely to be affected.[20]
In accordance with the involvement of androgens in seborrhoeic dermatitis, antiandrogens, such as cyproterone acetate,[33] spironolactone,[34] flutamide,[35][36] and nilutamide,[37][38] are highly effective in alleviating the condition.[30][39] As such, they are used in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis,[30][39] particularly severe cases.[40] While beneficial in seborrhoeic dermatitis, effectiveness may vary with different antiandrogens; for instance, spironolactone (which is regarded as a relatively weak antiandrogen) has been found to produce a 50% improvement after three months of treatment, whereas flutamide has been found to result in an 80% improvement within three months.[30][36] Cyproterone acetate, similarly more potent and effective than spironolactone, results in considerable improvement or disappearance of acne and seborrhoea in 90% of patients within three months.[41]
Systemic antiandrogen therapy is generally used to treat seborrhoeic dermatitis only in women, not in men, as these medications can result in feminization (e.g., gynecomastia), sexual dysfunction, and infertility in males.[42][43] In addition, antiandrogens theoretically have the potential to feminize male fetuses in pregnant women and, for this reason, are usually combined with effective birth control in sexually active women who can or may become pregnant.[41]
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are used primarily to reduce itching, if present. However, research studies suggest that some antihistamines have anti-inflammatory properties.[44]
Keratolytics
Keratolytics help the skin via exfoliation built-up skin flakes and thereby remove scale. They are applied topically to the affected area. Keratolytics include urea, salicylic acid, coal tar, lactic acid, pyrithione zinc and propylene glycol.[24] Coal tar shampoo formulations can be effective.[8][24] Although no significant increased risk of cancer in human treatment with coal tar shampoos has been found, caution is advised since coal tar is carcinogenic in animals, and heavy human occupational exposures do increase cancer risks.[45]
Other treatments
- Isotretinoin, a sebosuppressive agent, may be used to reduce sebaceous gland activity as a last resort in refractory disease.[29] However, isotretinoin has potentially serious side effects, and few patients with seborrhoeic dermatitis are appropriate candidates for therapy.[26]
- Topical 0.75% and 1% Metronidazole[10][11]
- Topical 4% nicotinamide[3]
- Topical sulfacetamide[11]
- Tea tree oil [12]
- Cannabidiol shampoo [24]
- Frequent washing to avoid the build-up of scale, especially on the scalp, but while avoiding overly drying the skin[12][11][20]
- Avoiding damaging skin with harsh grooming or chemical irritants[20]
Phototherapy
Another option is natural and artificial UV radiation since it can inhibit the growth of Malassezia yeast.[46] Some recommend photodynamic therapy using UV-A and UV-B laser or red and blue LED light to inhibit the growth of Malassezia fungus and reduce seborrhoeic inflammation.[46][47][48]
Outcome
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is generally a chronic and recurring condition. Individuals may have the condition for several weeks to months, but it may also last years or their lifetime. There may be periods of relapse and worsening.[11][8]
Epidemiology
Seborrhoeic dermatitis affects 1 to 5% of the general population.[1][49][50] It is slightly more common in men, but affected women tend to have more severe symptoms.[50] The condition usually recurs throughout a person's lifetime.[51] Seborrhoeic dermatitis can occur in any age group[51] but often occurs during the first three months of life then again at puberty and peaks in incidence at around 40 years of age.[52][20] It can reportedly affect as many as 31% of older people.[50] Infants may also have this condition, though it is typically milder, and is referred to as cradle cap.[12] Seborrhoeic dermatitis is more common in African-Americans.[12]
Severity is worse in dry climates[51] as well as hot weather as dry skin can exacerbate the condition.[12] COVID-19 related mask usage may also cause or exacerbate facial seborrhoeic dermatitis.[12]
Individuals who are immune compromised have increased risk of seborrhoeic dermatitis.[12] Conditions that are associated with increased rates of seborrhoeic dermatitis include individuals with HIV, hepatitis C, alcoholic pancreatitis, Parkinson's disease, and alcohol abuse.[12] Seborrhoeic dermatitis is common in people with alcoholism, between 7 and 11 percent, which is twice the normal expected occurrence.[53]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Seborrheic dermatitis: etiology, risk factors, and treatments: facts and controversies". Clinics in Dermatology 31 (4): 343–351. Jul–Aug 2013. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.001. PMID 23806151.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Seborrheic Dermatitis - Dermatologic Disorders". https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/dermatologic-disorders/dermatitis/seborrheic-dermatitis.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 "Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: a comprehensive review". The Journal of Dermatological Treatment 30 (2): 158–169. March 2019. doi:10.1080/09546634.2018.1473554. PMID 29737895.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 "Seborrhoeic dermatitis". British Journal of Hospital Medicine 78 (6): C88–C91. June 2017. doi:10.12968/hmed.2017.78.6.C88. PMID 28614013.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Cradle Cap". StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. August 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531463/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp". BMJ Clinical Evidence 2015. May 2015. PMID 26016669.
- ↑ "Seborrheic dermatitis". https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/scaly-skin/seborrheic-dermatitis.
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 8.10 8.11 8.12 8.13 8.14 8.15 8.16 8.17 "Dermatitis, Seborrheic". Quick Medical Diagnosis & Treatment 2023 (2023 ed.). McGraw-Hill Education. 2023. ISBN 978-1264687343.
- ↑ "Seborrheic Dermatitis: What is It, Diagnosis & Treatment". Cleveland, Ohio: Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14403-seborrheic-dermatitis.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 "Topical antifungals for seborrhoeic dermatitis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 4 (5): CD008138. May 2015. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008138.pub3. PMID 25933684.
- ↑ 11.00 11.01 11.02 11.03 11.04 11.05 11.06 11.07 11.08 11.09 11.10 11.11 11.12 11.13 11.14 11.15 11.16 11.17 11.18 11.19 11.20 11.21 Habif's Clinical Dermatology, Seventh Edition (7th ed.). Elsevier Inc. 2021. ISBN 978-0-323-61269-2.
- ↑ 12.00 12.01 12.02 12.03 12.04 12.05 12.06 12.07 12.08 12.09 12.10 12.11 12.12 12.13 12.14 12.15 12.16 12.17 12.18 12.19 12.20 12.21 12.22 "Unmet needs for patients with seborrheic dermatitis". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology: S0190–9622(22)03307–2. December 2022. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.12.017. PMID 36538948.
- ↑ "Dermatitis". http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/skin_disorders/itching_and_noninfectious_rashes/dermatitis.html.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 14.7 "Seborrheic dermatitis-Looking beyond Malassezia". Experimental Dermatology 28 (9): 991–1001. September 2019. doi:10.1111/exd.14006. PMID 31310695.
- ↑ "Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis". American Family Physician 61 (9): 2703–10, 2713–4. May 2000. PMID 10821151. http://www.aafp.org/afp/20000501/2703.html.
- ↑ "Seborrheic dermatitis". American Family Physician 52 (1): 149–55, 159–60. July 1995. PMID 7604759.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Seborrheic dermatitis: an overview". American Family Physician 74 (1): 125–130. July 2006. PMID 16848386. http://www.aafp.org/link_out?pmid=16848386. Retrieved 2010-04-15.
- ↑ "A Review of hormone-based therapies to treat adult acne vulgaris in women". International Journal of Women's Dermatology 3 (1): 44–52. March 2017. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.02.018. PMID 28492054.
- ↑ "Retrospective, observational study on the effects and tolerability of flutamide in a large population of patients with acne and seborrhea over a 15-year period". Gynecological Endocrinology 27 (10): 823–829. October 2011. doi:10.3109/09513590.2010.526664. PMID 21117864.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 20.6 20.7 "Seborrheic dermatitis: topical therapeutics and formulation design". European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 185: 148–164. April 2023. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.01.023. PMID 36842718.
- ↑ Therapeutic Use of Medicinal Plants and their Extracts: Volume 2: Phytochemistry and Bioactive Compounds. Springer. 2018. pp. 435. ISBN 978-3319923871.
- ↑ "Seborrhoeic dermatitis and dandruff (seborrheic eczema). DermNet NZ". . DermNet NZ. 2012-03-20. http://dermnetnz.org/dermatitis/seborrhoeic-dermatitis.html.
- ↑ "Clinical Characteristics and Quality of Life of Seborrheic Dermatitis Patients in a Tropical Country". Indian Journal of Dermatology 60 (5): 519. September 2015. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.164410. PMID 26538714.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 24.3 24.4 "Scalp Seborrheic Dermatitis: What We Know So Far". Skin Appendage Disorders 9 (3): 160–164. June 2023. doi:10.1159/000529854. PMID 37325288.
- ↑ "Topical anti-inflammatory agents for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face or scalp". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017 (5): CD009446. May 2014. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009446.pub2. PMID 24838779.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Systematic review of oral treatments for seborrheic dermatitis". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 28 (1): 16–26. January 2014. doi:10.1111/jdv.12197. PMID 23802806.
- ↑ "Seborrhoeic dermatitis | DermNet NZ" (in en). https://dermnetnz.org/topics/seborrhoeic-dermatitis.
- ↑ "Seborrhoea is not a feature of seborrhoeic dermatitis". British Medical Journal 286 (6372): 1169–1170. April 1983. doi:10.1136/bmj.286.6372.1169. PMID 6220754.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Low-dose oral isotretinoin for moderate to severe seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis: a randomized comparative trial". International Journal of Dermatology 56 (1): 80–85. January 2017. doi:10.1111/ijd.13408. PMID 27778328.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 "Androgen receptor antagonists (antiandrogens): structure-activity relationships". Current Medicinal Chemistry 7 (2): 211–247. February 2000. doi:10.2174/0929867003375371. PMID 10637363.
- ↑ "Androgen action on human skin -- from basic research to clinical significance". Experimental Dermatology 13 (s4): 5–10. 2004. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2004.00255.x. PMID 15507105.
- ↑ "Androgen Physiology, Pharmacology, Use and Misuse". Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.. October 2020.
- ↑ Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2001. pp. 1004–. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=FVfzRvaucq8C&pg=PA1004.
- ↑ ACNE and ROSACEA. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 66,685,687. ISBN 978-3-642-59715-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=0cD-CAAAQBAJ&pg=PA66.
- ↑ Diagnosis and Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Springer Science & Business Media. 27 February 2009. pp. 240–. ISBN 978-0-387-09718-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=fgMYVxmPDnMC&pg=PA240.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "Current aspects of antiandrogen therapy in women". Current Pharmaceutical Design 5 (9): 707–23 (717). September 1999. doi:10.2174/1381612805666230111201150. PMID 10495361. https://books.google.com/books?id=9rfNZL6oEO0C&pg=PA717.
- ↑ "Effects of a pure antiandrogen on gonadotropin secretion in normal women and in polycystic ovarian disease". Fertility and Sterility 52 (1): 42–50. July 1989. doi:10.1016/s0015-0282(16)60786-0. PMID 2744186.
- ↑ "Clinical applications of antiandrogens". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry 31 (4B): 719–729. October 1988. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(88)90023-4. PMID 2462132.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 Drug Actions: Basic Principles and Therapeutic Aspects. CRC Press. 1995. pp. 304–. ISBN 978-0-8493-7774-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=IvN4mZxraMkC&pg=PA304.
- ↑ Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach. McGraw Hill Professional. 6 July 2008. p. 1598. ISBN 978-0-07-164325-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=SnwB_fmjr2MC.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Androgens II and Antiandrogens / Androgene II und Antiandrogene. Springer Science & Business Media. 27 November 2013. pp. 351, 516. ISBN 978-3-642-80859-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=7JPsCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA351.
- ↑ Drug Therapy in Dermatology. CRC Press. 19 April 2016. pp. 295–. ISBN 978-0-203-90831-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=3TDMBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA295.
- ↑ The Clinical Nanomedicine Handbook. CRC Press. 13 December 2013. pp. 97–. ISBN 978-1-4398-3478-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=cWRmAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA97.
- ↑ "Antiinflammatory properties of cetirizine in a human contact dermatitis model. Clinical evaluation of patch tests is not hampered by antihistamines". Acta Dermato-Venereologica 78 (3): 194–197. May 1998. doi:10.1080/000155598441512. PMID 9602225.
- ↑ "No increased risk of cancer after coal tar treatment in patients with psoriasis or eczema". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology 130 (4): 953–961. April 2010. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.389. PMID 20016499.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 "The effect of UV-light on pityrosporum yeasts: ultrastructural changes and inhibition of growth". Acta Dermato-Venereologica 70 (1): 69–71. 1990. PMID 1967880.
- ↑ "A comprehensive overview of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of superficial fungal infections of the skin". Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology. B, Biology 78 (1): 1–6. January 2005. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2004.06.006. PMID 15629243.
- ↑ "Antibacterial photodynamic therapy in dermatology". Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences (rsc.org) 3 (10): 907–917. October 2004. doi:10.1039/B407622B. PMID 15480480.
- ↑ Your Best Medicine: From Conventional and Complementary Medicine--Expert-Endorsed Therapeutic Solutions to Relieve Symptoms and Speed Healing. Rodale. 17 March 2009. pp. 462–. ISBN 978-1-60529-656-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=fZtCudGcuVwC&pg=PA462.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 Textbook of Aging Skin. Springer Science & Business Media. 2 December 2009. pp. 534–. ISBN 978-3-540-89655-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=9-ALWZhXomAC&pg=PA534.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 Smart Medicine for Your Skin: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Conventional and Alternative Therapies to Heal Common Skin Problems. Penguin. 2001. pp. 271–. ISBN 978-1-58333-098-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=DQEZvR-IPeIC&pg=PA271.
- ↑ "Improving the management of seborrhoeic dermatitis". The Practitioner 258 (1768): 23–6, 3. February 2014. PMID 24689165.
- ↑ "Skin diseases in alcoholics". Acta Dermatovenerologica Croatica 12 (3): 181–190. 2004. PMID 15369644. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/8344438.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |