Chemistry:Flurithromycin
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
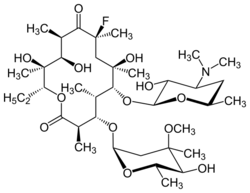
| Formula | C37H66FNO13 |
| Molar mass | 751.927 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Flurithromycin is a second generation macrolide antibiotic. It is a fluorinated derivative of erythromycin A.[1] It is a broad spectrum antibiotic with similar bactericidal action to erythromycin. Unlike erythromycin, flurithromycin is more tolerant of acidic environments, meaning more survives the digestion process, resulting in higher serum levels, and more efficacious elimination of susceptible bacteria, including staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pyogenes.[2]
References
- ↑ "In vitro activity of flurithromycin, a novel macrolide antibiotic". Chemioterapia 5 (3): 177–184. June 1986. PMID 3487389.
- ↑ "7.18 - Macrolide Antibiotics" (in en). Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry II. Oxford: Elsevier. January 2007. pp. 519–566. doi:10.1016/b0-08-045044-x/00219-4. ISBN 978-0-08-045044-5.
 |

