Chemistry:Adipic acid dihydrazide
From HandWiki
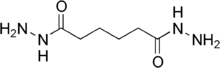
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexanedihydrazide | |
| Other names
Adipic dihydrazide
Adipohydrazide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | ADH |
| 973863 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Adipic+dihydrazide |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 174.20 g/mol |
| Melting point | 176 to 185 °C (349 to 365 °F; 449 to 458 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Material Safety Data Sheet |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
hexanedioic acid hexanedihydrazide hexanedioyl dichloride hexanedinitrile hexanediamide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Adipic acid dihydrazide (ADH) is a chemical used for cross-linking water-based emulsions. It can also be used as a hardener for certain epoxy resins.[2] ADH is a symmetrical molecule with a C4 backbone, and the reactive group is C=ONHNH2. Dihydrazides are made by the reaction of an organic acid with hydrazine. Other dihydrazides with different backbones are also common, including isophthalic dihydrazide (IDH) and sebacic dihydrazide (SDH).
References
External links
- Preparation of Enzyme Conjugate through Adipic Acid Dihydrazide as Linker
- Ďurana, R; Bystrický, S (2002). "Preparation and characterization of adipic acid dihydrazide derivatives of yeast mannans". Carbohydrate Polymers 50 (2): 177. doi:10.1016/S0144-8617(02)00020-6.
- Technical Article About the Chemistry and Use of Dihydrazides in Thermosets, Including ADH
 |

