Biology:Chromosome 8
| Chromosome 8 | |
|---|---|
 Human chromosome 8 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 8 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 146,259,331 (CHM13)[1] |
| No. of genes | 646 (CCDS)[2] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric[3] (45.2 Mbp[4]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 8 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 8 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 8 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 8 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000008 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000670 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 8 spans about 146 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 4.5 and 5.0% of the total DNA in cells.[5]
About 8% of its genes are involved in brain development and function, and about 16% are involved in cancer. A unique feature of 8p is a region of about 15 megabases that appears to have a high mutation rate. This region shows a significant divergence between human and chimpanzee, suggesting that its high mutation rates have contributed to the evolution of the human brain.[5]
Genes
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 8. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[6]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 646 | — | — | [2] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 656 | 242 | 539 | [7] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 670 | 1,052 | 613 | [8] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 703 | — | — | [9] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 719 | 848 | 682 | [10][11][12] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 8. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases and disorders are some of those related to genes on chromosome 8:
- 8p23.1 duplication syndrome
- Burkitt lymphoma
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
- COACH syndrome
- Cleft lip and cleft palate
- Cohen syndrome
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Fahr's syndrome
- Hereditary multiple exostoses
- Lipoprotein lipase deficiency, familial
- Myelodysplastic syndrome
- Pfeiffer syndrome
- Primary microcephaly
- Rothmund–Thomson syndrome
- Schizophrenia, associated with 8p21-22 locus[13][14][15]
- Waardenburg syndrome
- Werner syndrome
- Pingelapese blindness
- Langer–Giedion syndrome
- Roberts syndrome
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Sanfilippo syndrome
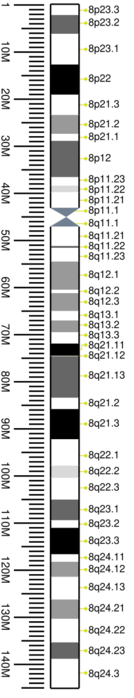
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[20] | Band[21] | ISCN start[22] |
ISCN stop[22] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[23] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | p | 23.3 | 0 | 115 | 1 | 2,300,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | p | 23.2 | 115 | 331 | 2,300,001 | 6,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 8 | p | 23.1 | 331 | 690 | 6,300,001 | 12,800,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | p | 22 | 690 | 992 | 12,800,001 | 19,200,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 8 | p | 21.3 | 992 | 1179 | 19,200,001 | 23,500,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | p | 21.2 | 1179 | 1380 | 23,500,001 | 27,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 8 | p | 21.1 | 1380 | 1639 | 27,500,001 | 29,000,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | p | 12 | 1639 | 1897 | 29,000,001 | 36,700,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 8 | p | 11.23 | 1897 | 2041 | 36,700,001 | 38,500,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | p | 11.22 | 2041 | 2156 | 38,500,001 | 39,900,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 8 | p | 11.21 | 2156 | 2343 | 39,900,001 | 43,200,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | p | 11.1 | 2343 | 2472 | 43,200,001 | 45,200,000 | acen | |
| 8 | q | 11.1 | 2472 | 2645 | 45,200,001 | 47,200,000 | acen | |
| 8 | q | 11.21 | 2645 | 2817 | 47,200,001 | 51,300,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 11.22 | 2817 | 3033 | 51,300,001 | 51,700,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 8 | q | 11.23 | 3033 | 3277 | 51,700,001 | 54,600,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 12.1 | 3277 | 3493 | 54,600,001 | 60,600,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 8 | q | 12.2 | 3493 | 3622 | 60,600,001 | 61,300,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 12.3 | 3622 | 3809 | 61,300,001 | 65,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 8 | q | 13.1 | 3809 | 3938 | 65,100,001 | 67,100,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 13.2 | 3938 | 4096 | 67,100,001 | 69,600,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 8 | q | 13.3 | 4096 | 4312 | 69,600,001 | 72,000,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 21.11 | 4312 | 4545 | 72,000,001 | 74,600,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 8 | q | 21.12 | 4545 | 4628 | 74,600,001 | 74,700,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 21.13 | 4628 | 4858 | 74,700,001 | 83,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 8 | q | 21.2 | 4858 | 4959 | 83,500,001 | 85,900,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 21.3 | 4959 | 5289 | 85,900,001 | 92,300,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 8 | q | 22.1 | 5289 | 5577 | 92,300,001 | 97,900,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 22.2 | 5577 | 5692 | 97,900,001 | 100,500,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 8 | q | 22.3 | 5692 | 5922 | 100,500,001 | 105,100,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 23.1 | 5922 | 6152 | 105,100,001 | 109,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 8 | q | 23.2 | 6152 | 6267 | 109,500,001 | 111,100,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 23.3 | 6267 | 6611 | 111,100,001 | 116,700,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 8 | q | 24.11 | 6611 | 6726 | 116,700,001 | 118,300,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 24.12 | 6726 | 6942 | 118,300,001 | 121,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 8 | q | 24.13 | 6942 | 7244 | 121,500,001 | 126,300,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 24.21 | 7244 | 7431 | 126,300,001 | 130,400,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 8 | q | 24.22 | 7431 | 7661 | 130,400,001 | 135,400,000 | gneg | |
| 8 | q | 24.23 | 7661 | 7804 | 135,400,001 | 138,900,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 8 | q | 24.3 | 7804 | 8250 | 138,900,001 | 145,138,636 | gneg |
References
- ↑ "Homo sapiens isolate CHM13 chromosome 8". National Library of Medicine /accessdate=2023-01-13. 4 April 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/CP068270.2.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Search results - 8[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2016-09-08. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=8%5BChr%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22has%20ccds%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=dSwWBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA45.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Rubenstein JL; Rubenstein (2009). "Chromosome 8p as a potential hub for developmental neuropsychiatric disorders: implications for schizophrenia, autism and cancer". Mol Psychiatry 14 (6): 563–89. doi:10.1038/mp.2009.2. PMID 19204725.
- ↑ Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes.". Genome Biol 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMID 20441615.
- ↑ "Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 8". 2017-05-12. https://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/statistics?c=8.
- ↑ "Chromosome 8: Chromosome summary - Homo sapiens". 2017-03-29. http://mar2017.archive.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Location/Chromosome?r=8.
- ↑ "Human chromosome 8: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". 2018-02-28. https://www.uniprot.org/docs/humchr08.txt.
- ↑ "Search results - 8[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=8%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22genetype%20protein%20coding%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Search results - 8[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=8%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%28%22genetype%20miscrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20ncrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20rrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20trna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20scrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20snrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20snorna%22%5BProperties%5D%29%20NOT%20%22genetype%20protein%20coding%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Search results - 8[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=8%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22genetype%20pseudo%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Schizophrenia susceptibility loci on chromosomes 13q32 and 8p21". Nat. Genet. 20 (1): 70–3. September 1998. doi:10.1038/1734. PMID 9731535.
- ↑ "Genomewide genetic linkage analysis confirms the presence of susceptibility loci for schizophrenia, on chromosomes 1q32.2, 5q33.2, and 8p21-22 and provides support for linkage to schizophrenia, on chromosomes 11q23.3-24 and 20q12.1-11.23". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 68 (3): 661–73. March 2001. doi:10.1086/318788. PMID 11179014.
- ↑ "Genomewide linkage scan of 409 European-ancestry and African American families with schizophrenia: suggestive evidence of linkage at 8p23.3-p21.2 and 11p13.1-q14.1 in the combined sample". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78 (2): 315–33. February 2006. doi:10.1086/500272. PMID 16400611.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=lGCLrh0DIwEC.
- ↑ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images". 2012 Ninth International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE). pp. 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965. ISBN 978-1-4673-1921-8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261304470.
- ↑ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ↑ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ↑ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Gilbert F (2001). "Chromosome 8". Genet Test 5 (4): 345–54. doi:10.1089/109065701753617516. PMID 11960583.
- Nusbaum C et al. (2006). "DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 8". Nature 439 (7074): 331–5. doi:10.1038/nature04406. PMID 16421571. Bibcode: 2006Natur.439..331N.
External links
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 8". Genetics Home Reference. http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=8.
- "Chromosome 8". http://web.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/posters/chromosome/chromo08.shtml.
 |