Astronomy:IU Aurigae
From HandWiki
Short description: Triple star system in the constellation Auriga
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Auriga |
| Right ascension | 05h 27m 52.40539s[2] |
| Declination | +34° 46′ 58.3435″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.19 to 8.83[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B0p + B1Vp[3] + ? |
| U−B color index | -0.66 |
| B−V color index | 0.18 |
| Variable type | Eclipsing binary[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 9 ± 5 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −4.479[2] mas/yr Dec.: -9.049[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.4786 ± 0.5765[2] mas |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
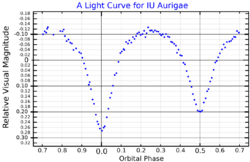
IU Aurigae is a triple star[6] system in the constellation Auriga, consisting of an eclipsing binary pair orbiting a third component with a period of 335 years.[7] This system is too faint to be viewed with the naked eye, having a peak apparent visual magnitude of 8.19.[3] The eclipsing pair form a Beta Lyrae-type semidetached binary of two Bp stars[3] with a period of 1.81147435 days.[4] During the primary eclipse, the visual magnitude of the system drops to 8.89, while for the secondary it decreases to 8.74.[3][8] The third component is a massive object with 17–18 M☉, and may actually be a binary – which would make this a quadruple star system.[7]
References
- ↑ Özdemir, S.; Mayer, P.; Drechsel, H.; Demircan, O.; Ak, H. (May 2003). "Refinement of third body parameters and new photometric results for the early-type multiple system IU Aurigae". Astronomy & Astrophysics 403 (2): 675–681. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030392. Bibcode: 2003A&A...403..675O.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Avvakumova, E. A. et al. (October 2013), "Eclipsing variables: Catalogue and classification", Astronomische Nachrichten 334 (8): 860, doi:10.1002/asna.201311942, Bibcode: 2013AN....334..860A
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, 5.1 61 (1): 80–88, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ "IU Aur". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=IU+Aur.
- ↑ Mayer, P.; Drechsel, H. (September 1987), "Up-to-date parameters of the eclipsing triple system IU AUR", Astronomy and Astrophysics 183 (1): 61–65, Bibcode: 1987A&A...183...61M.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.0 7.1 Drechsel, H.; Haas, S.; Lorenz, R.; Mayer, P. (April 1994), "New photometric and spectroscopic results for IU Aurigae -- an early-type eclipsing binary in a multiple system", Astronomy and Astrophysics 284 (3): 853–864, Bibcode: 1994A&A...284..853D.
- ↑ Watson, Christopher (January 4, 2010), "IU Aurigae", The International Variable Star Index (American Association of Variable Star Observers), http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=4000, retrieved 2019-08-18.
 |