Astronomy:9 Aurigae
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Auriga |
| Right ascension | 05h 06m 40.62967s[1] |
| Declination | +51° 35′ 51.8025″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.93 - 5.03[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F2V[3] |
| U−B color index | -0.03[4] |
| B−V color index | +0.34[4] |
| Variable type | γ Dor[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| A | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −0.47±0.57[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −28.557[6] mas/yr Dec.: −171.822[6] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 37.0551 ± 0.1371[6] mas |
| Distance | 88.0 ± 0.3 ly (26.99 ± 0.10 pc) |
| B | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −54.582[7] mas/yr Dec.: −156.009[7] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 37.0796 ± 0.0631[7] mas |
| Distance | 88.0 ± 0.1 ly (26.97 ± 0.05 pc) |
| C | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −1.88±0.17[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −32.386[8] mas/yr Dec.: −173.026[8] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 37.2115 ± 0.0184[8] mas |
| Distance | 87.65 ± 0.04 ly (26.87 ± 0.01 pc) |
| Orbit[9] | |
| Period (P) | 391.7 d |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.37 |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 5.8 km/s |
| Details | |
| A | |
| Mass | 1.97[10] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.56[5] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 6.042[11] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.07[5] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,023[5] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.12[5] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 21.0[5] km/s |
| B | |
| Mass | 0.49[10] M☉ |
| Temperature | 4,947[12] K |
| C | |
| Mass | 0.751[13] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.756[13] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.162[14] L☉ |
| Temperature | 4,633[14] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | 9 Aur A |
| 9 Aur B | |
| 9 Aur C | |
9 Aurigae (9 Aur) is a star system in the constellation Auriga. It has an apparent magnitude of about 5, making it visible to the naked eye in many suburban skies.[15] Parallax estimates made by the Hipparcos spacecraft put it at about 86 light-years (26 parsecs) from the Solar System,[1] although individual Gaia Data Release 3 parallaxes place all three components at 88 light years.
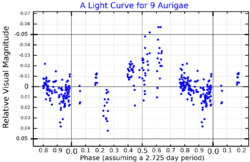
Kevin Krisciunas and Edward Francis Guinan discovered that the star is a variable star in 1990.[17] It is a well-studied Gamma Doradus variable,[5] and was one of the first stars to be so-classified.[18] This star type varies in luminosity due to non-radial pulsations.[18] Its apparent magnitude varies from 4.93 to 5.03 over a period of 1.25804 days.[2] For that reason it was given the variable star designation V398 Aurigae in 1995.[19][2]
9 Aurigae is a multiple star system. The naked-eye component A is a single-lined spectroscopic binary. Only the signature of an F-type main sequence star can be seen in the spectrum, but the periodic doppler shift of the absorption lines demonstrates that there is a hidden companion in a 391.7-day orbit. The gravitational interaction of the two bodies produces variations in their respective motions, which is what creates the doppler shift.[9]
Four other companions to 9 Aurigae are listed in multiple star catalogs.[20][21] The closest companion is a 12th-magnitude red dwarf 5″ away.[5] 90″ away is component C, a 9th-magnitude star with a spectral class of K5Ve,[22] which may also be a spectroscopic binary.[10] Further-separated still is a 14th-magnitude star, component D, proposed to be a more distant red giant,[23] although Gaia astrometry places it at a similar distance and with a similar proper motion.[24] The most widely-separated companion is component E, a distant unrelated star.[23][25]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Gray, R. O.; Corbally, C. J.; Garrison, R. F.; McFadden, M. T.; Bubar, E. J.; McGahee, C. E.; O'Donoghue, A. A.; Knox, E. R. (2006). "Contributions to the Nearby Stars (NStars) Project: Spectroscopy of Stars Earlier than M0 within 40 pc--The Southern Sample". The Astronomical Journal 132 (1): 161–170. doi:10.1086/504637. Bibcode: 2006AJ....132..161G.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mermilliod, J.-C. (1986). "Compilation of Eggen's UBV data, transformed to UBV (unpublished)". Catalogue of Eggen's UBV Data. Bibcode: 1986EgUBV........0M. http://cdsads.u-strasbg.fr/cgi-bin/nph-bib_query?1986EgUBV........0M&db_key=AST&nosetcookie=1.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Rachford, Brian L.; Foight, Dillon R. (2009). "Chromospheric Variability in Early F-Type Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 698 (1): 786–802. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/698/1/786. Bibcode: 2009ApJ...698..786R.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Abt, Helmut A. (1965). "The Frequency of Binaries among Normal A-Type Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 11: 429. doi:10.1086/190120. Bibcode: 1965ApJS...11..429A.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "HR 1637". http://www.ctio.noao.edu/~atokovin/stars/stars.php?cat=HR&number=1637.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Newton, Elisabeth R.; Irwin, Jonathan; Charbonneau, David; Berlind, Perry; Calkins, Michael L.; Mink, Jessica (2017). "The Hα Emission of Nearby M Dwarfs and its Relation to Stellar Rotation". The Astrophysical Journal 834 (1): 85. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/834/1/85. Bibcode: 2017ApJ...834...85N.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Bortle, John E. (February 2001). "The Bortle Dark-Sky Scale". Sky & Telescope. Sky Publishing Corporation. https://skyandtelescope.org/astronomy-resources/light-pollution-and-astronomy-the-bortle-dark-sky-scale/.
- ↑ Krisciunas, K.; Aspin, C.; Geballe, T. R.; Akazawa, H.; Claver, C. F.; Guinan, E. F.; Landis, H. J.; Luedeke, K. D. et al. (August 1993). "The 9 Aurigae system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 263 (3): 781–788. doi:10.1093/mnras/263.3.781. Bibcode: 1993MNRAS.263..781K.
- ↑ Krisciunas, K.; Guinan, E. (August 1990). "Unexplained Light Variations of the F0 V Star 9 Aurigae". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3511: 1–7. Bibcode: 1990IBVS.3511....1K. https://ibvs.konkoly.hu/pub/ibvs/3501/3511.pdf. Retrieved 1 December 2024.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Krisciunas, K.; Griffin, R. F.; Guinan, E. F.; Luedeke, K. D.; McCook, G. P. (1995). "9 Aurigae: Strong evidence for non-radial pulsations". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 273 (3): 662. doi:10.1093/mnras/273.3.662. Bibcode: 1995MNRAS.273..662K.
- ↑ Kazarovets, E. V.; Samus, N. N. (January 1995). "The 72nd Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 4140: 1–28. Bibcode: 1995IBVS.4140....1K. https://ibvs.konkoly.hu/pub/ibvs/4101/4140.pdf. Retrieved 1 December 2024.
- ↑ Dommanget, J.; Nys, O. (1994). "Catalogue des composantes d'etoiles doubles et multiples (CCDM) premiere edition - Catalogue of the components of double and multiple stars (CCDM) first edition". Com. De l'Observ. Royal de Belgique 115: 1. Bibcode: 1994CoORB.115....1D.
- ↑ Mason, Brian D.; Wycoff, Gary L.; Hartkopf, William I.; Douglass, Geoffrey G.; Worley, Charles E. (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal 122 (6): 3466–3471. doi:10.1086/323920. Bibcode: 2001AJ....122.3466M.
- ↑ Alonso-Floriano, F. J.; Morales, J. C.; Caballero, J. A.; Montes, D.; Klutsch, A.; Mundt, R.; Cortés-Contreras, M.; Ribas, I. et al. (2015). "CARMENES input catalogue of M dwarfs". Astronomy & Astrophysics 577: A128. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201525803. Bibcode: 2015A&A...577A.128A.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Krisciunas, K.; Aspin, C.; Geballe, T. R.; Akazawa, H.; Claver, C. F.; Guinan, E. F.; Landis, H. J.; Luedeke, K. D. et al. (1993). "The 9 Aurigae system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 263 (3): 781–788. doi:10.1093/mnras/263.3.781. Bibcode: 1993MNRAS.263..781K.
- ↑ Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
 |