Astronomy:KZ Andromedae
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Andromeda |
| Right ascension | 23h 09m 57.3642s[2] |
| Declination | +35° 32′ 55.65804″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.91 – 8.03 variable[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K2Ve+K2Ve[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 8.81[4] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.93[4] |
| Apparent magnitude (G) | 7.6580[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (J) | 6.225[5] |
| Apparent magnitude (H) | 5.778[5] |
| Apparent magnitude (K) | 5.659[5] |
| Variable type | BY Dra[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −5.818±0.026[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 150.123±0.063 [2] mas/yr Dec.: 1.226±0.059[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 32.8449 ± 0.0369[2] mas |
| Distance | 99.3 ± 0.1 ly (30.45 ± 0.03 pc) |
| Orbit[6] | |
| Period (P) | 3.03291126±0.00000046 days |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.01174±0.00056 |
| Periastron epoch (T) | HJD 2455133.480±0.020 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 7.11±2.35° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 69.362±0.046 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 71.300±0.054 km/s |
| Details[6] | |
| Primary | |
| Radius | 0.77±0.07 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.34±0.06 L☉ |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 12.5 km/s |
| Secondary | |
| Radius | 0.66±0.06 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.25±0.04 L☉ |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 12.2 km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
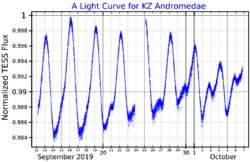
KZ Andromedae (often abbreviated to KZ And) is a double lined spectroscopic binary in the constellation Andromeda. Its apparent visual magnitude varies between 7.91 and 8.03 during a cycle slightly longer than 3 days.
System
Both stars in the KZ Andromedae system are main sequence stars of spectral type K2Ve, meaning that the spectrum shows strong emission lines.[3] This is caused by their active chromospheres that cause large spots on the surface.[6]
KZ Andromedae is listed in the Washington Double Star Catalog as the secondary component in a visual binary system, with the primary being HD 218739. In 50 years of observations, there is little evidence of relative motion between the two stars; however, they have a common proper motion and a similar radial velocity.[6]
Variability
The rotational velocity of both stars is consistent with a synchronous rotation of the pair, and the rotational period is itself comparable to the brightness variation period. KX Andromedae is thus classified as a BY Draconis variable, and the variability is caused by the large spots on the surface.[6]
References
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "KZ And database entry". Combined General Catalog of Variable Stars. CDS. http://webviz.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR-S?V*%20KZ%20And.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "KZ And". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=KZ+And.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Cutri, Roc M.; Skrutskie, Michael F.; Van Dyk, Schuyler D.; Beichman, Charles A.; Carpenter, John M.; Chester, Thomas; Cambresy, Laurent; Evans, Tracey E. et al. (2003). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: 2MASS All-Sky Catalog of Point Sources (Cutri+ 2003)". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 2246: II/246. Bibcode: 2003yCat.2246....0C. http://vizier.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR?-source=II/246.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Fekel, F. C.; Henry, G. W.; Tomkin, J. (September 2017). "New Precision Orbits of Bright Double-lined Spectroscopic Binaries. X. HD 96511, HR 7578, and KZ Andromedae". The Astronomical Journal 154 (3): 13. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa816e. 120. Bibcode: 2017AJ....154..120F.
 |