Astronomy:GR Andromedae
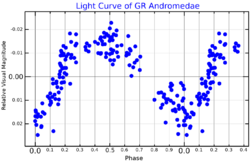
GR Andromedae (often abbreviated to GR And) is a variable star in the constellation Andromeda. Its apparent visual magnitude varies between 6.87 and 6.95 in a cycle of 518.2 days.[1] It is classified as an α2 Canum Venaticorum variable.[3]
Spectrum
The radiation emitted by GP Andromedae is a typical stellar blackbody with absorption lines from various elements, which gives to the star a spectral type A2pSrCrEu, meaning that unusually strong lines of strontium, chromium and europium can be observed.[3] GP Andromedae is thus classified as an Ap star. The intensity and profile of the spectral lines varies within a cycle with the same period as the brightness variations.[8]
Variability
Photometric and spectral variability of GR Andromedae is typical of a star with a strong and variable magnetic field. This way, the 518.2 days periodicity can be identified as the rotation period of the star.[8] It's among the slowest rotators in the category of magnetic chemically peculiar stars, with a calculated equatorial rotation rate of only 0.2 km/s.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Pyper, D. M.; Adelman, S. J. (October 2017). "On the Photometric Variability of Very Sharp-lined Cool mCP Stars". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 129 (980): 104203. doi:10.1088/1538-3873/aa7c9e. Bibcode: 2017PASP..129j4203P.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 GR And, database entry, Combined General Catalog of Variable Stars (GCVS4.2, 2004 Ed.), N. N. Samus, O. V. Durlevich, et al., CDS ID II/250 Accessed on line 2018-10-17.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "GR And". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=GR+And.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Cutri, Roc M.; Skrutskie, Michael F.; Van Dyk, Schuyler D.; Beichman, Charles A.; Carpenter, John M.; Chester, Thomas; Cambresy, Laurent; Evans, Tracey E. et al. (2003). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: 2MASS All-Sky Catalog of Point Sources (Cutri+ 2003)". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 2246: II/246. Bibcode: 2003yCat.2246....0C. http://vizier.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR?-source=II/246.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Kochukhov, O.; Bagnulo, S. (2006). "Evolutionary state of magnetic chemically peculiar stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 450 (2): 763. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054596. Bibcode: 2006A&A...450..763K.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Catalano, F. A.; Leone, F. (June 1990). "Photoelectric photometry of chemically peculiar stars at the Catania astrophysical observatory. Observatory of HD 2453, HD 71866, HD 72968 and HD 126515.". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 83: 491. Bibcode: 1990A&AS...83..491C.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Soubiran, Caroline et al. (2016), "The PASTEL catalogue: 2016 version", Astronomy & Astrophysics 591: A118, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628497, Bibcode: 2016A&A...591A.118S.
 |