Astronomy:Zeta Andromedae
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Andromeda |
| Right ascension | 00h 47m 20.32547s[1] |
| Declination | +24° 16′ 01.8408″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.92 to 4.14[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K1III + KV[3] |
| U−B color index | +0.90[4] |
| B−V color index | +1.12[4] |
| R−I color index | +0.59[4] |
| Variable type | ELL/RS[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −24.43 ± 0.1[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −101.17[1] mas/yr Dec.: −81.77[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 17.24 ± 0.26[1] mas |
| Distance | 189 ± 3 ly (58.0 ± 0.9 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +0.14[3] |
| Orbit[3] | |
| Period (P) | 17.769426 |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 2.7 R* |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.0 |
| Inclination (i) | 65 ± 5° |
| Details | |
| Aa | |
| Mass | 2.6 ± 0.4[3] M☉ |
| Radius | 15.9 ± 0.8[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 95.5[3] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.8[3] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,665 ± 140[6] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.30[3] dex |
| Rotation | 17.77 days[7] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 41.4 ± 0.2[3] km/s |
| Ab | |
| Mass | 0.75[3] M☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Coordinates: ![]() 00h 47m 20.3254s, +24° 16′ 01.841″
Zeta Andromedae (Zeta And, ζ Andromedae, ζ And) is a star system in the constellation Andromeda. It is approximately 189 light-years from Earth.
00h 47m 20.3254s, +24° 16′ 01.841″
Zeta Andromedae (Zeta And, ζ Andromedae, ζ And) is a star system in the constellation Andromeda. It is approximately 189 light-years from Earth.
Zeta Andromedae is the star's Bayer designation. It also has the Flamsteed designation 34 Andromedae and multiple other designations in stellar catalogues.
Location
The star's location is in the northern constellation Andromeda, in which it is the second-most southerly of the stars in this often drawn characteristic shape representing the mythical princess asterism, after η Andromedae.
System
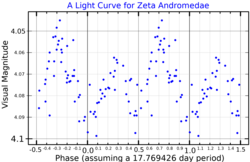
The system is a spectroscopic binary whose primary is classified as an orange K-type giant with a mean apparent magnitude of +4.08. Due to brightness changes caused by the ellipsoidal shape of that object, the system is also an RS Canum Venaticorum-type variable star. Its brightness varies from magnitude +3.92 to +4.14 with a period of 17.77 days, and its spectrum shows strong and variable Ca II H and K lines.[3] The orbital period of the binary is 17.77 days.
Direct imaging
The primary component of this binary system, Zeta Andromedae Aa, is one of the few stars who has been imaged directly using Doppler imaging and long-baseline infrared interferometry. With direct imaging we can recover additional information about this star.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Oblateness | 1.060 ± 0.011 |
| Polar radius | 15.0 ± 0.8 R☉ |
| Axis Inclination[lower-alpha 1] | 70.0 ± 2.8 ° |
| Pole angle[lower-alpha 2] | 126 ± 1.9 ° |
Direct imaging also allowed observation of starspots (the analogue to sunspots), on this star, and their asymmetric distribution showed that the magnetic field of the star is generated by a mechanism different from the solar dynamo.[9] A Sun-like differential rotation of the star was observed instead.[3]
Visual companions
The WDS notes three visual companions to the eclipsing binary (Aa and Ab, forming binary A).[4] The parallax of the D star has been measured by Gaia proving its distance to be much greater than Zeta Andromedae, probably a distant red giant.[10] The closest companion, B, is likewise a background object.[11] The companion C at 97″ shares a common proper motion and a similar parallax.[12]
|
Naming
In Chinese, 奎宿 (Kuí Sù), meaning Legs (asterism), refers to an asterism consisting of ζ Andromedae, η Andromedae, 65 Piscium, ε Andromedae, δ Andromedae, π Andromedae, ν Andromedae, μ Andromedae, β Andromedae, σ Piscium, τ Piscium, 91 Piscium, υ Piscium, φ Piscium, χ Piscium and ψ1 Piscium. Consequently, the Chinese name for ζ Andromedae itself is 奎宿二 (Kuí Sù èr, English: the Second Star of Legs).[14]
Notes
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 zet And, database entry, The combined table of GCVS Vols I-III and NL 67-78 with improved coordinates, General Catalogue of Variable Stars , Sternberg Astronomical Institute, Moscow, Russia. Accessed on line August 29, 2008.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 Kővári, Zs.; Bartus, J.; Strassmeier, K. G.; Oláh, K.; Weber, M.; Rice, J. B.; Washuettl, A. (2007). "Doppler imaging of stellar surface structure. XXIII. The ellipsoidal K giant binary ζ Andromedae". Astronomy and Astrophysics 463 (3): 1071. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065982. Bibcode: 2007A&A...463.1071K.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 HR 215, database entry, The Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Preliminary Version), D. Hoffleit and W. H. Warren, Jr., CDS ID V/50. Accessed on line August 29, 2008.
- ↑ Karataș, Yüksel; Bilir, Selçuk; Eker, Zeki; Demircan, Osman; Liebert, James; Hawley, Suzanne L.; Fraser, Oliver J.; Covey, Kevin R. et al. (2004). "Kinematics of chromospherically active binaries and evidence of an orbital period decrease in binary evolution". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 349 (3): 1069–1092. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07588.x. Bibcode: 2004MNRAS.349.1069K.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Korhonen, H.; Wittkowski, M.; Kovári, Zs.; Granzer, Th.; Hackman, T.; Strassmeier, K. G. (2010). "Ellipsoidal primary of the RS CVn binary ζ Andromedae . Investigation using high-resolution spectroscopy and optical interferometry". Astronomy and Astrophysics 515: A14. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913736. Bibcode: 2010A&A...515A..14K.
- ↑ Strassmeier, Klaus G. (September 2009), "Starspots", The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review 17 (3): 251–308, doi:10.1007/s00159-009-0020-6, Bibcode: 2009A&ARv..17..251S
- ↑ Kővári, Zsolt; Oláh, Katalin; Bartus, János; Strassmeier, Klaus G.; Granzer, Thomas (August 2006). "Spot Modelling of ζ Andromedae". Astrophysics and Space Science 304 (1–4): 55–57. doi:10.1007/s10509-006-9073-4. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233843354. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Roettenbacher, R.M.; Monnier, J.D.; Korhonen, H.; Aarnio, A.N.; Baron, F.; Che, X.; Harmon, R.O.; Kővári, Zs. et al. (2016). "No Sun-like dynamo on the active star ζ Andromedae from starspot asymmetry". Nature 533 (7602): 217–220. doi:10.1038/nature17444. PMID 27144357. Bibcode: 2016Natur.533..217R.
- ↑ Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Entry 00473+2416, The Washington Double Star Catalog , United States Naval Observatory. Accessed on line August 29, 2008.
- ↑ (in Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 5 月 19 日
External links
- Zeta Andromedae at Alcyone Software's Star Data Pages
- Image ζ Andromedae
- Rachael Roettenbacher, "How the face of a distant star reveals our place in the cosmos," Aeon Magazine [retrieved July 27, 2016]
 |