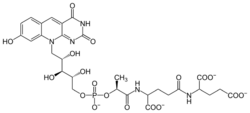
Biology:Coenzyme F420
Coenzyme F420 is a family of coenzymes involved in redox reactions in a number of bacteria and archaea. It is derived from coenzyme FO (7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin) and differs by having a oligoglutamyl tail attached via a 2-phospho-L-lactate bridge. F420 is so named because it is a flavin derivative with an absorption maximum at 420 nm.
F420 was originally discovered in methanogenic archaea[1] and in Actinomycetota (especially in Mycobacterium).[2] It is now known to be used also by Cyanobacteria and by soil Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi and Firmicutes.[3] Eukaryotes including the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster and the algae Ostreococcus tauri also use Coenzyme FO.[4]
F420 is structurally similar to FMN, but catalytically it is similar to NAD and NADP: it has low redox potential and always transfer a hydride. As a result, it is not only a versatile cofactor in biochemical reactions, but also being eyed for potential as an industrial catalyst. Similar to FMN, it has two states: one reduced state, notated as F420-H2, and one oxidized state, written as just F420.[5] FO has largely similar redox properties, but cannot carry an electric charge and as a result probably slowly leaks out of the cellular membrane.[3]
A number of F420 molecules, differing by the length of the oligoglutamyl tail, are possible; F420-2, for example, refers to the version with two glutamyl units attached. Lengths from 4 to 9 are typical.[3]
Biosynthesis
Coenzyme F420 is synthesized via a multi-step pathway:
- 7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin synthase (FbiC) produces Coenzyme FO (also written F0), itself a cofactor of DNA photolyase (antenna). This is the head portion of the molecule.[4]
- 2-phospho-L-lactate transferase (FbiA) produces Coenzyme F420-0, the portion containing the head, the diphosphate bridge, and ending with a carboxylic acid group.
- Coenzyme F420-0 (one part of FbiB) puts a glutamate residue at the -COOH end, producing Coenzyme F420-1.
- Coenzyme F420-1 (other part of FbiB) puts a gamma-glutamate residue at the -COOH end, producing Coenzyme F420-2, the final compound (in its oxidized form). Also responsible for adding additional units.
Oxidized F420 can be converted to reduced F420-H2 by multiple enzymes such as Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (coenzyme-F420) (Fgd1).[5]
Function
The coenzyme is a substrate for coenzyme F420 hydrogenase,[6] 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase and methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase.[7][8]
A long list of other enzymes use F420 to oxidize (dehydrogenate) or F420-H2 to reduce substrates.[5]
Clinical relevance
Delamanid, a drug used to treat multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDRTB) in combination with other antituberculosis medications, is activated in the mycobacterium by deazaflavin-dependent nitroreductase (Ddn), an enzyme which uses dihydro-F420 (reduced form). The activated form of the drug is highly reactive and attacks cell wall synthesis enzymes such as DprE2. Pretomanid works in the same way. Clinical isolates resistant to these two drugs tend to have mutations in the biosynthetic pathway for F420.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ "Redox-driven proton translocation in methanogenic Archaea". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 59 (9): 1513–33. September 2002. doi:10.1007/s00018-002-8526-3. PMID 12440773.
- ↑ "Unexpected abundance of coenzyme F(420)-dependent enzymes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other actinobacteria". Journal of Bacteriology 192 (21): 5788–98. November 2010. doi:10.1128/JB.00425-10. PMID 20675471.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Ney, B; Ahmed, FH; Carere, CR; Biswas, A; Warden, AC; Morales, SE; Pandey, G; Watt, SJ et al. (January 2017). "The methanogenic redox cofactor F(420) is widely synthesized by aerobic soil bacteria.". The ISME Journal 11 (1): 125–137. doi:10.1038/ismej.2016.100. PMID 27505347. Bibcode: 2017ISMEJ..11..125N.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "The archaeal cofactor F0 is a light-harvesting antenna chromophore in eukaryotes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106 (28): 11540–5. July 2009. doi:10.1073/pnas.0812665106. PMID 19570997. Bibcode: 2009PNAS..10611540G.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Grinter, Rhys; Greening, Chris (8 September 2021). "Cofactor F420: an expanded view of its distribution, biosynthesis and roles in bacteria and archaea". FEMS Microbiology Reviews 45 (5). doi:10.1093/femsre/fuab021. PMID 33851978.
- ↑ "8-Hydroxy-5-deazaflavin-reducing hydrogenase from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: 1. Purification and characterization". Biochemistry 26 (14): 4219–27. July 1987. doi:10.1021/bi00388a007. PMID 3663585.
- ↑ "Coenzyme F420-dependent methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase (Mtd) from Methanopyrus kandleri: a methanogenic enzyme with an unusual quarternary structure". Journal of Molecular Biology 332 (5): 1047–57. October 2003. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00949-5. PMID 14499608.
- ↑ "Purification and properties of 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase and 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase, two coenzyme F420-dependent enzymes, from Methanosarcina barkeri". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology 1079 (3): 293–302. September 1991. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(91)90072-8. PMID 1911853.
- ↑ Abrahams, Katherine A.; Batt, Sarah M.; Gurcha, Sudagar S.; Veerapen, Natacha; Bashiri, Ghader; Besra, Gurdyal S. (28 June 2023). "DprE2 is a molecular target of the anti-tubercular nitroimidazole compounds pretomanid and delamanid". Nature Communications 14 (1): 3828. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-39300-z. PMID 37380634. Bibcode: 2023NatCo..14.3828A.
External links
- KEGG:
 |