Chemistry:Cytidine triphosphate
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cytidine 5′-(tetrahydrogen triphosphate)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-Amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl} tetrahydrogen triphosphate | |
| Other names
CTP; Cytidine-5'-triphosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Cytidine+triphosphate |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H16N3O14P3 | |
| Molar mass | 483.156 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
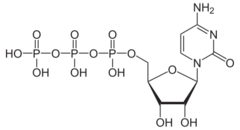
Cytidine triphosphate (CTP) is a pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate. CTP, much like ATP, consists of a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups. The major difference between the two molecules is the base used, which in CTP is cytosine.
CTP is a substrate in the synthesis of RNA.
CTP is a high-energy molecule similar to ATP, but its role as an energy coupler is limited to a much smaller subset of metabolic reactions. CTP is a coenzyme in metabolic reactions like the synthesis of glycerophospholipids, where it is used for activation and transfer of diacylglycerol and lipid head groups,[1] and glycosylation of proteins.
CTP acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme aspartate carbamoyltransferase, which is used in pyrimidine biosynthesis.[2]
See also
- CTP synthase
- Cytidine
- Cytosine
- Pyrimidine biosynthesis
References
- ↑ Buchanan, Bob B.; Gruissem, Wilhelm; Jones, Russell L. (2000). Biochemistry & molecular biology of plants (1st ed.). American society of plant physiology. ISBN 978-0-943088-39-6. https://archive.org/details/biochemistrymole00buch.
- ↑ Blackburn, G. Michael. Nucleic Acids in Chemistry and Biology. The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2006, p. 119-120.
 |

