Chemistry:Carglumic acid
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
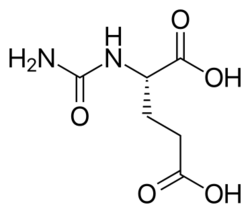 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Carbaglu, Ucedane |
| Other names | (S)-2-ureidopentanedioic acid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30% |
| Protein binding | Undetermined |
| Metabolism | Partial |
| Elimination half-life | 4.3 to 9.5 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (60%) and kidney (9%, unchanged) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H10N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 190.155 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Carglumic acid, sold under the brand name Carbaglu among others, is used for the treatment of hyperammonaemia.[2][5][6]
Carglumic acid is a carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS 1) activator.[2]
The most common adverse effects include vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia (fever), and tonsillitis, anemia, diarrhea, ear infection, other infections, nasopharyngitis, decreased hemoglobin levels, and headache.[2]
It was approved for medical use in the United States in March 2010.[7] Carglumic acid is an orphan drug.[8][9] It is available as a generic medication.[10]
Medical uses
Carglumic acid is indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia and chronic hyperammonemia.[2][3][4]
References
- ↑ "Prescription medicines: registration of new chemical entities in Australia, 2015". 21 June 2022. https://www.tga.gov.au/prescription-medicines-registration-new-chemical-entities-australia-2015.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Carbaglu- carglumic acid tablet". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=10175e73-5172-4dde-a508-8a88b7afc0a1.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Carbaglu EPAR". 17 September 2018. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/carbaglu.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Ucedane EPAR". 17 September 2018. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/ucedane.
- ↑ "Restoration of ureagenesis in N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency by N-carbamylglutamate". J Pediatr 145 (4): 552–4. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.06.047. PMID 15480384.
- ↑ "N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency and the treatment of hyperammonemic encephalopathy". Ann Neurol 52 (6): 845–9. 2002. doi:10.1002/ana.10406. PMID 12447942.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Carbaglu (Carglumic Acid) Tablets". 16 February 2010. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2010/022562s000TOC.cfm.
- ↑ "Carglumic acid Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". 17 June 2014. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=352111.
- ↑ "Carglumic acid Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". 20 January 1998. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=109997.
- ↑ "Competitive Generic Therapy Approvals". 29 June 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/generic-drugs/competitive-generic-therapy-approvals.
External links
- "Carglumic acid". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/carglumic%20acid.
 |
