Chemistry:Lithium cyanide
From HandWiki
Short description: Toxic crystalline salt
| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UN number | 1935 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| LiCN | |||
| Molar mass | 32.959 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White Powder | ||
| Density | 1.073 g/cm3 (18 °C) | ||
| Melting point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) Dark coloured | ||
| Boiling point | decomposes | ||
| Soluble | |||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
N/A | ||
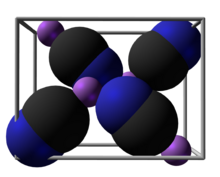
| Structure | |||
| - | |||
| Fourfold | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | 742899 | ||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H226, H300, H310, H330, H410 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+310, P302+350, P303+361+353, P304+340, P310, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 57 °C (135 °F; 330 K) | ||
| N/A | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Sodium cyanide, Potassium cyanide, Hydrogen cyanide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Lithium cyanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiCN. It is a toxic, white coloured, hygroscopic, water-soluble salt that finds only niche uses.
Preparation
LiCN is produced from the reaction of lithium hydroxide and hydrogen cyanide. A laboratory-scale preparation uses acetone cyanohydrin as a surrogate for HCN:[5]
- (CH3)2C(OH)CN + LiH → (CH3)2CO + LiCN + H2
Uses
The compound decomposes to cyanamide and carbon when heated to a temperature close to but below 600 °C. Acids react to give hydrogen cyanide.[6]
Lithium cyanide can be used as a reagent for organic compound cyanation.[7]
- RX + LiCN → RCN + LiX
References
- ↑ J. A. Lely, J. M. Bijvoet (1942), "The Crystal Structure of Lithium Cyanide", Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 61, London: WILEY-VCH Verlag, doi:10.1002/recl.19420610402
- ↑ Haynes, W.M (2013), "Bernard Lewis", in Bruno, Thomas., Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (93 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: Fitzroy Dearborn, http://www.hbcpnetbase.com/, retrieved 2012-12-09
- ↑ Material Safety Data Sheet: Lithium Cyanide, 0.5M Solution in N,N-Dimethylformamide, Fisher Scientific, 16 June 1999, http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/MSDS/MSDS/DisplayMSDSPage.do?country=US&language=en&productNumber=742899&brand=ALDRICH&PageToGoToURL=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sigmaaldrich.com%2Fcatalog%2Fproduct%2FALDRICH%2F742899%3Flang%3Den
- ↑ "Lithium cyanide" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/75478#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Livinghouse, Tom (1981). "Trimethylsilyl Cyanide: Cyanosilylation of p-Benzoquinone". Org. Synth. 60: 126. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.060.0126.
- ↑ L. Pesce (2010). "Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology". Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0325011416051903.a01.pub2. ISBN 978-0471238966.
- ↑ Harusawa, Shinya; Yoneda, Ryuji; Omori, Yukie; Kurihara, Takushi (1987). "Non-aqueous cyanation of halides using lithium cyanide". Tetrahedron Letters (Elsevier) 28 (36): 4189–4190. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)95575-8.
 |