Chemistry:Sergliflozin etabonate
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
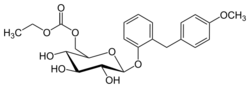
| Formula | C23H28O9 |
| Molar mass | 448.468 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Sergliflozin etabonate (INN/USAN,[1][2] codenamed GW869682X) is an investigational anti-diabetic drug being developed by GlaxoSmithKline. It did not undergo further development after phase II.[citation needed]
Method of action
Sergliflozin inhibits subtype 2 of the sodium-glucose transport proteins (SGLT2), which is responsible for at least 90% of the glucose reabsorption in the kidney. Blocking this transporter causes blood glucose to be eliminated through the urine.[3][4]
Chemistry
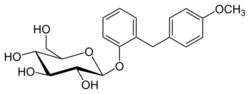
Etabonate refers to the ethyl carbonate group. The remaining structure, which is the active substance, is called sergliflozin.
References
- ↑ World Health Organization (2008). "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 59". WHO Drug Information 22 (1): 66. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/druginfo/INN_2008_list59.pdf.
- ↑ "Statement on a nonproprietary name adopted by the USAN council: Sergliflozin etabonate". American Medical Association. http://www.ama-assn.org/ama1/pub/upload/mm/365/sergliflozin_etabona.pdf. Retrieved 2008-08-10.
- ↑ "Sergliflozin, a novel selective inhibitor of low-affinity sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT2), validates the critical role of SGLT2 in renal glucose reabsorption and modulates plasma glucose level". J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320 (1): 323–30. January 2007. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.110296. PMID 17050778. http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/cgi/content/full/320/1/323.
- ↑ "Prous Science: Molecule of the Month November 2007". http://www.prous.com/molecules/default.asp?ID=165.
 |

