Chemistry:Scandium acetate
From HandWiki
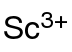
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Scandium(III) acetate
Scandium ethanoate Scandium(III) ethanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H9O6Sc | |
| Molar mass | 222.088 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Scandium acetate is an inorganic compound, with the chemical formula of Sc(CH3COO)3. It exists in the anhydrous and the hydrate forms. It can be obtained by reacting scandium hydroxide with aqueous acetic acid.[1] It is a water-soluble crystal that decomposes into scandium oxide at high temperature.[2] It can be used to prepare other scandium-containing materials.[3]
References
- ↑ V. N. Krasil’nikov, O. I. Gyrdasova, I. V. Baklanova, L. A. Perelyaeva, E. F. Zhilina, É. G. Vovkotrub (May 2012). "Structure and luminescence properties of nanostructured solid-state solutions of Sc1–x Eu x (CH3CO2)3" (in en). Theoretical and Experimental Chemistry 48 (2): 113–117. doi:10.1007/s11237-012-9247-9. ISSN 0040-5760. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11237-012-9247-9. Retrieved 2020-02-20.
- ↑ Elements, American. "Scandium Acetate" (in en). https://www.americanelements.com/scandium-acetate-3804-23-7.
- ↑ Xin, Chengrong; Zhang, Qilong; Yang, Hui. Synthesis and Properties Study of BaTi0.95Sc0.05O3-δ Nanopowders and Ceramics. Piezoelectrics & Acoustooptics, 2013, 35(3):412-415. (in Chinese)
Acetyl halides and salts of the acetate ion
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcOH | He | ||||||||||||||||||
| LiOAc | Be(OAc)2 BeAcOH |
B(OAc)3 | AcOAc ROAc |
NH4OAc | AcOOH | FAc | Ne | ||||||||||||
| NaOAc | Mg(OAc)2 | Al(OAc)3 ALSOL Al(OAc)2OH Al2SO4(OAc)4 |
Si | P | S | ClAc | Ar | ||||||||||||
| KOAc | Ca(OAc)2 | Sc(OAc)3 | Ti(OAc)4 | VO(OAc)3 | Cr(OAc)2 Cr(OAc)3 |
Mn(OAc)2 Mn(OAc)3 |
Fe(OAc)2 Fe(OAc)3 |
Co(OAc)2, Co(OAc)3 |
Ni(OAc)2 | Cu(OAc)2 | Zn(OAc)2 | Ga(OAc)3 | Ge | As(OAc)3 | Se | BrAc | Kr | ||
| RbOAc | Sr(OAc)2 | Y(OAc)3 | Zr(OAc)4 | Nb | Mo(OAc)2 | Tc | Ru(OAc)2 Ru(OAc)3 Ru(OAc)4 |
Rh2(OAc)4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc | Cd(OAc)2 | In | Sn(OAc)2 Sn(OAc)4 |
Sb(OAc)3 | Te | IAc | Xe | ||
| CsOAc | Ba(OAc)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(OAc)2 | Au | Hg2(OAc)2, Hg(OAc)2 |
TlOAc Tl(OAc)3 |
Pb(OAc)2 Pb(OAc)4 |
Bi(OAc)3 | Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| La(OAc)3 | Ce(OAc)x | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm(OAc)3 | Eu(OAc)3 | Gd(OAc)3 | Tb | Dy(OAc)3 | Ho(OAc)3 | Er | Tm | Yb(OAc)3 | Lu(OAc)3 | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(OAc)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||
 |

