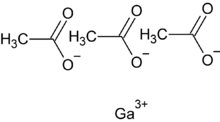
Chemistry:Gallium acetate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Tetra-μ2-acetatodiaquadigallium(III), diacetyloxygallanyl acetate
gallium(3+) triacetate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ga(O2C2H3)3 | |
| Molar mass | 246.85[1] |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Density | 1.57 g/cm/3 |
| Melting point | N/A |
| Boiling point | 117.1C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H314, H335 | |
| P261, P280, P305+351+338, P304+340, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |

Gallium acetate is a salt composed of a gallium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions where gallium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It has a chemical formula of Ga(CH3COO)3 although it can be informally referred to as GaAc because Ac is an informal symbol for acetate. Gallium is moderately water-soluble and decomposes to gallium oxide when heated to around 70 °C.[2] Gallium acetate, like other acetate compounds, is a good precursor to ultra-pure compounds, catalysts and nanoscale materials.[2] Gallium acetate is being considered as a substitute in de-icing compounds like calcium chloride and magnesium chloride.[3]
Preparation
Gallium acetate can be formed using a neutralization reaction (acetic acid reacts with gallium oxide or gallium hydroxide):
- 6CH3COOH + Ga2O3 → 2Ga(CH3COO)3 + 3H2O
- 3CH3COOH + Ga(OH)3 → Ga(CH3COO)3 + 3H2O
Gallium can also be refluxed in acetic acid for several weeks to produce gallium acetate.[4]
Applications
It can also be used in conjunction with acetylacetonate bis(thiosemicarbazone) to create radiogallium-acetylacetonate bis(thiosemicarbazone) complex. It can be used in tumor imaging.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ "Gallium acetate". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Gallium-acetate.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Elements, American. "Gallium Acetate" (in en). https://www.americanelements.com/gallium-acetate-2571-06-4.
- ↑ "Gallium acetate, 99.9% 2571-06-4 - Manufacturers & Suppliers in India with worldwide shipping.". https://www.ottokemi.com/gallium-compounds/gallium-acetate-pure.aspx.
- ↑ Funk, H.; Paul, A. Chemistry of gallium. II. Reactions between gallium and organic compounds. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie (1965), 337(3-4), 142-4.
- ↑ Jalilian, Amir R.; Yousefnia, Hassan; Garousi, Javad; Novinrouz, Aytak; Rajamand, Amir A.; Shafaee, Kamaledin (2009). "The development of radiogallium-acetylacetonate bis(thiosemicarbazone) complex for tumour imaging". Nuclear Medicine Review 12 (2): 65–71. ISSN 1644-4345. https://journals.viamedica.pl/nuclear_medicine_review/article/view/15208.
Acetyl halides and salts of the acetate ion
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcOH | He | ||||||||||||||||||
| LiOAc | Be(OAc)2 BeAcOH |
B(OAc)3 | AcOAc ROAc |
NH4OAc | AcOOH | FAc | Ne | ||||||||||||
| NaOAc | Mg(OAc)2 | Al(OAc)3 ALSOL Al(OAc)2OH Al2SO4(OAc)4 |
Si | P | S | ClAc | Ar | ||||||||||||
| KOAc | Ca(OAc)2 | Sc(OAc)3 | Ti(OAc)4 | VO(OAc)3 | Cr(OAc)2 Cr(OAc)3 |
Mn(OAc)2 Mn(OAc)3 |
Fe(OAc)2 Fe(OAc)3 |
Co(OAc)2, Co(OAc)3 |
Ni(OAc)2 | Cu(OAc)2 | Zn(OAc)2 | Ga(OAc)3 | Ge | As(OAc)3 | Se | BrAc | Kr | ||
| RbOAc | Sr(OAc)2 | Y(OAc)3 | Zr(OAc)4 | Nb | Mo(OAc)2 | Tc | Ru(OAc)2 Ru(OAc)3 Ru(OAc)4 |
Rh2(OAc)4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc | Cd(OAc)2 | In | Sn(OAc)2 Sn(OAc)4 |
Sb(OAc)3 | Te | IAc | Xe | ||
| CsOAc | Ba(OAc)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(OAc)2 | Au | Hg2(OAc)2, Hg(OAc)2 |
TlOAc Tl(OAc)3 |
Pb(OAc)2 Pb(OAc)4 |
Bi(OAc)3 | Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| La(OAc)3 | Ce(OAc)x | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm(OAc)3 | Eu(OAc)3 | Gd(OAc)3 | Tb | Dy(OAc)3 | Ho(OAc)3 | Er | Tm | Yb(OAc)3 | Lu(OAc)3 | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(OAc)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||
 |
