Chemistry:Nickel(II) acetate
From HandWiki

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Nickel(2+) diacetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6NiO4 | |
| Molar mass | 176.781 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Green Solid |
| Odor | slight acetic acid |
| Density | 1.798 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.744 g/cm3 (tetrahydrate) |
| Melting point | decomposes when heated [1][2] |
| Easily soluble in cold water, hot water | |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol insoluble in diethyl ether, n-octanol |
| +4,690.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/c | |
a = 4.764, b = 11.771, c = 8.425 Å α = 90°, β = 93.6°, γ = 90°[3] tetrahydrate
| |
Lattice volume (V)
|
471.5 |
Formula units (Z)
|
2 |
| distorted octahedral | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
350 mg/kg (rat, oral) 410 mg/kg (mouse, oral)[4] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
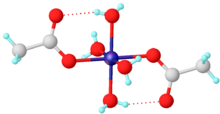
Nickel(II) acetate is the name for the coordination compounds with the formula Ni(CH3CO2)2·x H2O where x can be 0, 2, and 4. The green tetrahydrate Ni(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O is most common. It is used for electroplating.
Synthesis and structure
The compound can be prepared by treating nickel or nickel(II) carbonate with acetic acid:
- NiCO3 + 2 CH3CO2H + 3 H2O → Ni(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O + CO2
The green tetrahydrate has been shown by X-ray crystallography to adopt an octahedral structure, the central nickel centre being coordinated by four water molecules and two acetate ligands.[5] It may be dehydrated in vacuo, by reaction with acetic anhydride[6] or by heat.[7]
Safety
Nickel salts are carcinogenic and irritate the skin.
References
- ↑ M. A. Mohamed, S. A. Halawy, M. M. Ebrahim: "Non-isothermal decomposition of nickel acetate tetrahydrate", in: Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 1993, 27 (2), S. 109–110. doi:10.1016/0165-2370(93)80002-H.
- ↑ G. A. M. Hussein, A. K. H. Nohman, K. M. A. Attyia: "Characterization of the decomposition course of nickel acetate tetrahydrate in air", in: Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 1994, 42, S. 1155–1165; doi:10.1007/BF02546925.
- ↑ Downie, T. C.; Harrison, W.; Raper, E. S.; Hepworth, M. A. (15 March 1971). "A three-dimensional study of the crystal structure of nickel acetate tetrahydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section B 27 (3): 706–712. doi:10.1107/S0567740871002802. Bibcode: 1971AcCrB..27..706D.
- ↑ "Nickel metal and other compounds (as Ni)". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/7440020.html.
- ↑ Van Niekerk, J. N.; Schoening, F. R. L. (1953). "The crystal structures of nickel acetate, Ni(CH3COO)2·4H2O, and cobalt acetate, Co(CH3COO)2·4H2O". Acta Crystallogr. 6 (7): 609–612. doi:10.1107/S0365110X5300171X.
- ↑ Lascelles, Keith; Morgan, Lindsay G.; Nicholls, David; Beyersmann, Detmar (2005). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_235.pub2.
- ↑ Tappmeyer, W. P.; Davidson, Arthur W. (1963). "Cobalt and Nickel Acetates in Anhydrous Acetic Acid". Inorg. Chem. 2 (4): 823–825. doi:10.1021/ic50008a039.
Acetyl halides and salts of the acetate ion
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcOH | He | ||||||||||||||||||
| LiOAc | Be(OAc)2 BeAcOH |
B(OAc)3 | AcOAc ROAc |
NH4OAc | AcOOH | FAc | Ne | ||||||||||||
| NaOAc | Mg(OAc)2 | Al(OAc)3 ALSOL Al(OAc)2OH Al2SO4(OAc)4 |
Si | P | S | ClAc | Ar | ||||||||||||
| KOAc | Ca(OAc)2 | Sc(OAc)3 | Ti(OAc)4 | VO(OAc)3 | Cr(OAc)2 Cr(OAc)3 |
Mn(OAc)2 Mn(OAc)3 |
Fe(OAc)2 Fe(OAc)3 |
Co(OAc)2, Co(OAc)3 |
Ni(OAc)2 | Cu(OAc)2 | Zn(OAc)2 | Ga(OAc)3 | Ge | As(OAc)3 | Se | BrAc | Kr | ||
| RbOAc | Sr(OAc)2 | Y(OAc)3 | Zr(OAc)4 | Nb | Mo(OAc)2 | Tc | Ru(OAc)2 Ru(OAc)3 Ru(OAc)4 |
Rh2(OAc)4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc | Cd(OAc)2 | In | Sn(OAc)2 Sn(OAc)4 |
Sb(OAc)3 | Te | IAc | Xe | ||
| CsOAc | Ba(OAc)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(OAc)2 | Au | Hg2(OAc)2, Hg(OAc)2 |
TlOAc Tl(OAc)3 |
Pb(OAc)2 Pb(OAc)4 |
Bi(OAc)3 | Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| La(OAc)3 | Ce(OAc)x | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm(OAc)3 | Eu(OAc)3 | Gd(OAc)3 | Tb | Dy(OAc)3 | Ho(OAc)3 | Er | Tm | Yb(OAc)3 | Lu(OAc)3 | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(OAc)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||
 |


