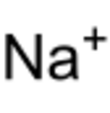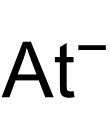Chemistry:Sodium astatide
From HandWiki
Short description: Inorganic compound of sodium and astatine
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Sodium astatide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| Properties | |||
| NaAt | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Magnesium astatide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Sodium astatide is a binary inorganic compound of sodium and astatine with the chemical formula NaAt.[1][2]
Synthesis
Sodium astatide solution has been prepared by distilling astatine from the bismuth alpha-ray target where it was prepared, dissolving in sodium bicarbonate solution, and reducing At+ and At3+ ions with ascorbic acid.[3]
Uses
Sodium astatide has been proposed for use in radiation therapy to replace 131I.[4][3]
References
- ↑ Watabe, Tadashi; Hosono, Makoto; Kinuya, Seigo; Yamada, Takahiro; Yanagida, Sachiko; Namba, Masao; Nakamura, Yoshihide (July 2021). "Manual on the proper use of sodium astatide ([211AtNaAt) injections in clinical trials for targeted alpha therapy (1st edition)"]. Annals of Nuclear Medicine 35 (7): 753–766. doi:10.1007/s12149-021-01619-2. ISSN 1864-6433. PMID 33978932.
- ↑ Ball, Philip (17 March 2020). "An affinity for astatine" (in en). https://www.chemistryworld.com/opinion/an-affinity-for-astatine/4011290.article.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Y. Shirakami. "Preparation of [211At-labeled sodium astatide (NaAt) by reducing with ascorbic acid for the treatment of thyroid cancer"]. RIKEN Accel. Prog. Rep. 53: 171. https://www.nishina.riken.jp/researcher/APR/APR053/pdf/171.pdf. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ↑ "Breakthrough alpha-ray treatment of cancer without external radiation" (in en). EurekAlert!. https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/915620.
 |