Chemistry:Lentinan
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Molar mass | ~ 500,000 Da |
| | |
Lentinan is a polysaccharide isolated from the fruit body of shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes).
Chemistry
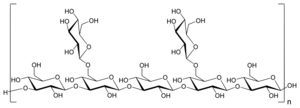
Lentinan is a β-1,3 beta-glucan with β-1,6 branching. It has a molecular weight of 500,000 Da and specific rotation of +14-22° (NaOH).
Research
Preclinical studies
An in vitro experiment showed lentinan stimulated production of white blood cells in the human cell line U937.[1] Lentinan is thought to be inactive in humans when given orally and is therefore administered intravenously. The authors of an in vivo study of lentinan suggested that the compound may be active when administered orally in mice.[2]
Human clinical trials
Lentinan has been the subject of a limited number of clinical studies in cancer patients in Japan;[3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10] however, evidence of efficacy is lacking.[11][12]
Adverse effects
Lentinan has been reported to cause shiitake mushroom dermatitis.[13]
See also
- Medicinal mushrooms
References
- ↑ "Effects of shiitake (Lentinus edodes) extract on human neutrophils and the U937 monocytic cell line". Phytotherapy Research 13 (2): 133–137. March 1999. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1573(199903)13:2<133::AID-PTR398>3.0.CO;2-O. PMID 10190187.
- ↑ "Inhibition of human colon carcinoma development by lentinan from shiitake mushrooms (Lentinus edodes)". Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 8 (5): 581–589. October 2002. doi:10.1089/107555302320825093. PMID 12470439.
- ↑ "Clinical application of a combination therapy of lentinan, multi-electrode RFA and TACE in HCC". Advances in Therapy 25 (8): 787–794. August 2008. doi:10.1007/s12325-008-0079-x. PMID 18670743.
- ↑ "[S-1 combined with lentinan in patients with unresectable or recurrent gastric cancer]" (in ja). Gan to Kagaku Ryoho. Cancer & Chemotherapy 33 Suppl 1 (1): 106–109. June 2006. PMID 16897983.
- ↑ "A multi-institutional prospective study of lentinan in advanced gastric cancer patients with unresectable and recurrent diseases: effect on prolongation of survival and improvement of quality of life. Kanagawa Lentinan Research Group". Hepato-Gastroenterology 46 (28): 2662–2668. 1999. PMID 10522061.
- ↑ "Individual patient based meta-analysis of lentinan for unresectable/recurrent gastric cancer". Anticancer Research 29 (7): 2739–2745. July 2009. PMID 19596954.
- ↑ "Efficacy of orally administered superfine dispersed lentinan (beta-1,3-glucan) for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer". Anticancer Research 29 (7): 2611–2617. July 2009. PMID 19596936. http://ar.iiarjournals.org/content/29/7/2611.full.
- ↑ "Lentinan with S-1 and paclitaxel for gastric cancer chemotherapy improve patient quality of life". Hepato-Gastroenterology 56 (90): 547–550. 2009. PMID 19579640.
- ↑ "Clinical efficacy of superfine dispersed lentinan (beta-1,3-glucan) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma". Hepato-Gastroenterology 56 (90): 437–441. 2009. PMID 19579616.
- ↑ "Efficacy of oral administered superfine dispersed lentinan for advanced pancreatic cancer". Hepato-Gastroenterology 56 (89): 240–244. 2009. PMID 19453066.
- ↑ "Lentinan". WebMD. http://www.webmd.com/vitamins-supplements/ingredientmono-763-lentinan.aspx?activeingredientid=763&activeingredientname=lentinan.
- ↑ "Lentinan". Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/integrative-medicine/herbs/lentinan.
- ↑ "Shiitake (Lentinus edodes) dermatitis". Contact Dermatitis 27 (2): 65–70. August 1992. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb05211.x. PMID 1395630.
External links
 |

