Chemistry:Ambuphylline
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
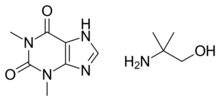
| IUPAC name
1,3-dimethyl-7H-purine-2,6-dione : 2-amino-2-methylpropan-1-ol
| |
| Other names
Theophylline aminoisobutanol, bufylline
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H19N5O3 | |
| Molar mass | 269.30 g/mol |
| Appearance | Crystalline, slightly yellowish white powder |
| Melting point | 254 to 256 °C (489 to 493 °F; 527 to 529 K) |
| Freely soluble. | |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | R03DA10 (WHO) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ambuphylline (or bufylline) is a combination of theophylline and aminoisobutanol used as a bronchodilator.[1] It also acts and may be used as a diuretic.[2]
References
- ↑ Smith, J. R.; Jensen, J. (1946). "The effect of theophylline aminoisobutanol in the failing experimental heart". The Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 31: 455–457. PMID 21022557.
- ↑ Dictionary querymondofacto.com
 |

