Chemistry:Chromium acetate hydroxide
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Chromium(III) acetate hydroxide
| |
| Other names
Acetic acid of the chromium salt,
Chromium(III)acetatehydroxide,Cr24%, Chromic acetate hydroxide, Chromium - acetic acid (3:7) dihydrate, Chromium Acetic Acid, Ccris 6345, | |
| Identifiers | |
| Properties | |
| C24H48Cr8O36 | |
| Molar mass | 1328.581 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | violet solid |
| Density | 1.484 g/cm3 |
| soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed, Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin |
| Safety data sheet | MSDS |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H315, H317, H319, H332, H335 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
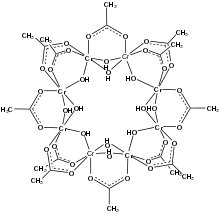
Chromium acetate hydroxide is the coordination complex with the formula [Cr2(OH)3(OAc)3]4. A dark violet solid, it crystallizes as the triacontatetrahydrate (34 molecules of water of crystallization). It is water soluble.[1]
Structure
The complex is a tetramer of binuclear Cr2(OH)3(OAc)3. The subunits are linked by acetate and hydroxide ligands. The oxidation state of chromium is III, which explains the stability of the complex since octahedral d3 ions give kinetically robust complexes. Overall, the complex's structure is unusual compared to other transition metal carboxylate complexes.
See also
References
- ↑ Eshel, Michal; Bino, Avi; Felner, Israel; Johnston, David C.; Luban, Marshall; Miller, Lance L. (2000). "Polynuclear Chromium(III) Carboxylates. 1. Synthesis, Structure, and Magnetic Properties of an Octanuclear Complex with a Ring Structure". Inorganic Chemistry 39 (7): 1376–1380. doi:10.1021/ic9907009. PMID 12526439.
External links
- http://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB9726110.htm
- http://www.chemicalbook.com/CAS%5Cmol%5C39430-51-8.mol
- https://web.archive.org/web/20120119193658/http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/ProductDetail.do?D7=0&N5=SEARCH_CONCAT_PNO%7CBRAND_KEY&N4=318108%7CALDRICH&N25=0&QS=ON&F=SPEC
Acetyl halides and salts of the acetate ion
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcOH | He | ||||||||||||||||||
| LiOAc | Be(OAc)2 BeAcOH |
B(OAc)3 | AcOAc ROAc |
NH4OAc | AcOOH | FAc | Ne | ||||||||||||
| NaOAc | Mg(OAc)2 | Al(OAc)3 ALSOL Al(OAc)2OH Al2SO4(OAc)4 |
Si | P | S | ClAc | Ar | ||||||||||||
| KOAc | Ca(OAc)2 | Sc(OAc)3 | Ti(OAc)4 | VO(OAc)3 | Cr(OAc)2 Cr(OAc)3 |
Mn(OAc)2 Mn(OAc)3 |
Fe(OAc)2 Fe(OAc)3 |
Co(OAc)2, Co(OAc)3 |
Ni(OAc)2 | Cu(OAc)2 | Zn(OAc)2 | Ga(OAc)3 | Ge | As(OAc)3 | Se | BrAc | Kr | ||
| RbOAc | Sr(OAc)2 | Y(OAc)3 | Zr(OAc)4 | Nb | Mo(OAc)2 | Tc | Ru(OAc)2 Ru(OAc)3 Ru(OAc)4 |
Rh2(OAc)4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc | Cd(OAc)2 | In | Sn(OAc)2 Sn(OAc)4 |
Sb(OAc)3 | Te | IAc | Xe | ||
| CsOAc | Ba(OAc)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(OAc)2 | Au | Hg2(OAc)2, Hg(OAc)2 |
TlOAc Tl(OAc)3 |
Pb(OAc)2 Pb(OAc)4 |
Bi(OAc)3 | Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| La(OAc)3 | Ce(OAc)x | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm(OAc)3 | Eu(OAc)3 | Gd(OAc)3 | Tb | Dy(OAc)3 | Ho(OAc)3 | Er | Tm | Yb(OAc)3 | Lu(OAc)3 | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(OAc)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||
 |

