Chemistry:Furoxan
From HandWiki
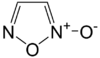
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2λ5,5-Oxadiazol-2-one | |
| Other names
Furazan N-oxide; Furazan 2-oxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C528141 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 86.050 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Furoxan or 1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide is a heterocycle of the isoxazole family and an amine oxide derivative of furazan. It is a nitric oxide donor.[1] As such, furoxan and its derivatives are actively researched as potential new drugs (Ipramidil) and insensitive high density explosives (4,4’-Dinitro-3,3’-diazenofuroxan).
Furoxanes can be formed by dimerization of nitrile oxides.
References
- ↑ Clara Cena; Massimo Bertinaria; Donatella Boschi; Marta Giorgis; Alberto Gasco (2006). "Use of the furoxan (1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide) system in the design of new NO-donor antioxidant hybrids". Arkivoc (HL-1787GR): 301–309. http://www.arkat-usa.org/ark/journal/2006/I07_ICHC-20/1787/HL-1787GR%20as%20published%20mainmanuscript.pdf.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
 |
