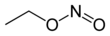
Chemistry:Ethyl nitrite
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl nitrite | |||
| Other names
1-Nitrosooxyethane
Ethyl alcohol nitrite Nitrous acid Nitrous ether Ethyl ester Nitrethyl | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H5NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 75.067 g·mol−1 | ||
| Boiling point | 17 °C (63 °F; 290 K) | ||
| 5.07 g/100 ml | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | [1] | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
The chemical compound ethyl nitrite is an alkyl nitrite with a chemical formula C2H5NO2. It may be prepared from ethanol.[2]
Uses
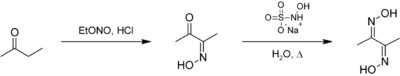
It is used as a reagent with butanone to yield the dimethylglyoxime end product.
Ethyl nitrite is the main ingredient in a traditional ethanol-based South African remedy for colds and flu known as Witdulsies, which is sold in pharmacies. It is known as a traditional Afrikaans remedy; the same remedy is apparently made by the Amish in the US. However, FDA has blocked over-the-counter sales of this same remedy, known in the US as sweet nitrite or sweet spirit of nitre, since 1980.[3] Its use has been associated with fatal methemoglobinemia.[4]
Methemoglobinemia is the primary toxic effect of ethyl nitrite.[5] Due to ethyl nitrite's high volatility and faint smell, in the presence of ethyl nitrite vapors, it is easy to breath a high dose of it without realizing, resulting in methemoglobinemia,[6] which may or may not be severe, or even fatal.
References
- ↑ "NFPA 704 Ratings for Common Chemicals". http://www.newenv.com/resources/nfpa_chemicals/.
- ↑ Semon, W. L.; Damerell, V. R. (1943). "Dimethylglyoxime". Organic Syntheses. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv2p0204.; Collective Volume, 2, pp. 204
- ↑ "Rulemaking History for OTC Sweet Spirits of Nitre Drug Products". fda.gov. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/DevelopmentResources/Over-the-CounterOTCDrugs/StatusofOTCRulemakings/ucm072140.htm.
- ↑ "ETHYL NITRITE - National Library of Medicine HSDB Database". https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/a?dbs+hsdb:@term+@DOCNO+416. "Archived copy". https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/a?dbs+hsdb:@term+@DOCNO+416.
- ↑ "Ethyl nitrite". Haz-Map. https://www.haz-map.com/Agents/1476.
- ↑ Titov, V Yu; Petrenko, Yu M (2005). "Proposed mechanism of nitrite-induced methemoglobinemia". Biochemistry (Moscow) 70 (4): 473–83. doi:10.1007/s10541-005-0139-7. PMID 15892615. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15892615/.
External links
 |