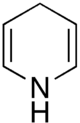
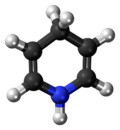
Chemistry:Dihydropyridine
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,4-Dihydropyridine[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| MeSH | 1,4-dihydropyridine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H7N | |||
| Molar mass | 81.1158 g mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Dihydropyridine (DHP) is a molecule based upon pyridine, and the parent of a class of molecules that have been semi-saturated with two substituents replacing one double bond. They are particularly well known in pharmacology as L-type calcium channel blockers, used in the treatment of hypertension. Compared with certain other L-type calcium channel blockers (for example those of the phenylalkylamine class such as verapamil) that have significant action at the heart, they are relatively vascular selective in their mechanism of action in lowering blood pressure.
Class members
Dihydropyridine class L-type calcium channel blockers include, in alphabetical order (brand names vary in different countries):
| Name | Image | Brand name |
| Amlodipine | 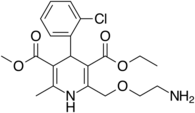 |
Norvasc, Istin, Normodipine, Tenox, Cordi Cor |
| Aranidipine | 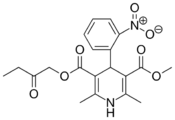 |
Sapresta (サプレスタ) |
| Azelnidipine | 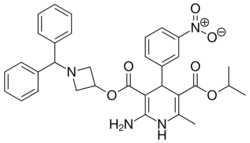 |
CalBlock (カルブロック) |
| Barnidipine | 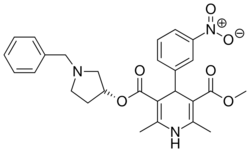 |
Vasexten, Libradin, Cyress, HypoCa |
| Benidipine | 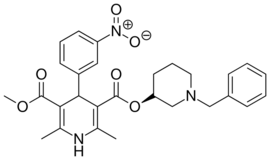 |
Coniel |
| Cilnidipine | 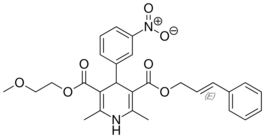 |
Atelec (アテレック), Cilacar, Cinalong, Siscard |
| Clevidipine | 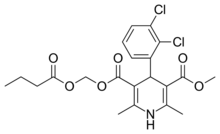 |
Cleviprex |
| Cronidipine | 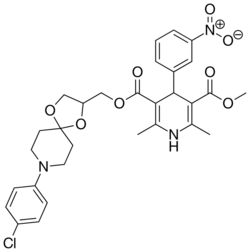 |
|
| Darodipine | 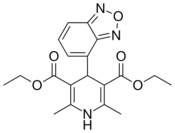 |
|
| Dexniguldipine | 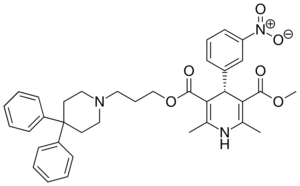 |
|
| Efonidipine | 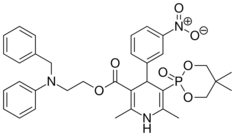 |
Landel (ランデル) |
| Elgodipine | 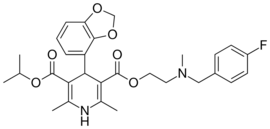 |
|
| Elnadipine | 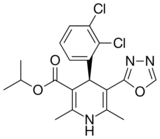 |
|
| Felodipine | 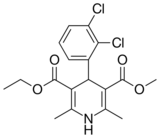 |
Renedil, Plendil |
| Flordipine | 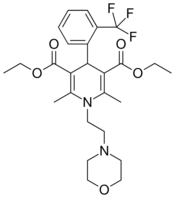 |
|
| Furnidipine | 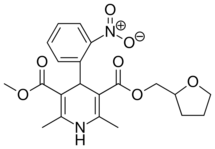 |
|
| Iganidipine | 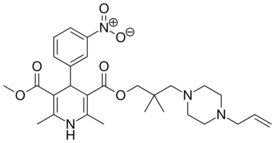 |
|
| Isradipine | 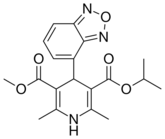 |
DynaCirc CR |
| Lacidipine |  |
Lacipil, Motens, Sakure |
| Lemildipine | 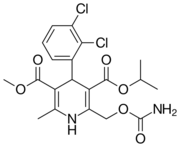 |
|
| Lercanidipine | 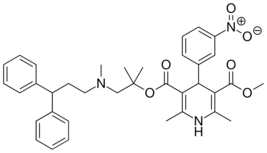 |
Zanidip, Zanidip-Recordati |
| Levamlodipine | 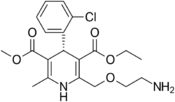 |
EsCordi Cor |
| Levniguldipine | 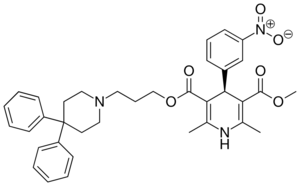 |
|
| Manidipine | 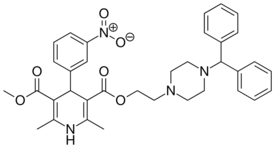 |
Manyper, Caslot, Madipine |
| Nicardipine | 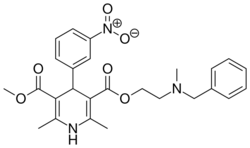 |
Cardene, Cardene SR |
| Nifedipine | 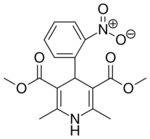 |
Adalat, Nifedical, Procardia, Corinfar, Cordaflex |
| Niguldipine | 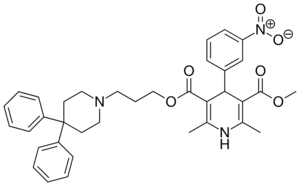 |
|
| Niludipine | 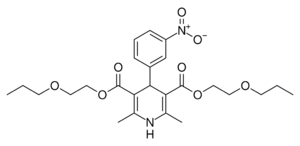 |
|
| Nilvadipine | 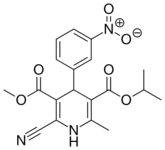 |
Nivadil |
| Nimodipine | 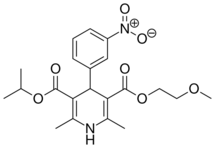 |
Nimotop |
| Nisoldipine | 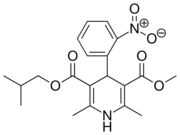 |
Sular, Baymycard, Syscor |
| Nitrendipine | 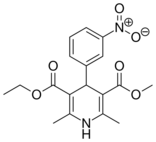 |
Baypress, Cardif, Nitrepin, Baylotensin |
| Olradipine | 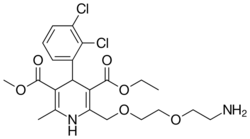 |
|
| Oxodipine | 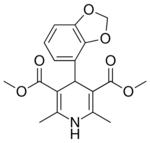 |
|
| Palonidipine | 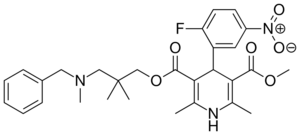 |
|
| Pranidipine |  |
Acalas |
| Ryodipine | 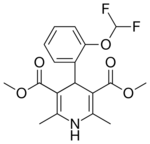 |
|
| Sagandipine | 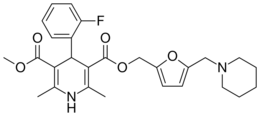 |
|
| Sornidipine | 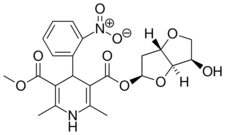 |
|
| Teludipine |  |
|
| Tiamdipine | 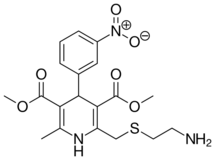 |
|
| Trombodipine | 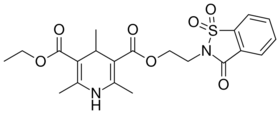 |
|
| Vatanidipine | 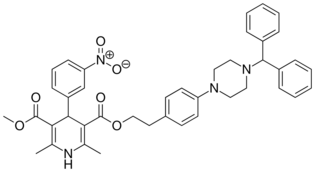 |
The pharmaceutical drug finerenone is also a dihydrophyridine derivative, but does not act as a calcium channel blocker but as an antimineralocorticoid.
See also
- Calcium channel blocker (including section on non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers)
- Calcium channel
- Dihydropyridine receptor
References
- ↑ "1,4-dihydropyridine - Compound Summary". Pubchem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 27 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=104822&loc=ec_rcs. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
External links
- Dihydropyridines at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)