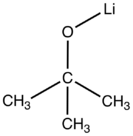
Chemistry:Lithium tert-butoxide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Lithium tert-butoxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H9LiO | |
| Molar mass | 80.06 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 0.918 g/cm3 (hexamer) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | strong base |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H228, H251, H302, H314 | |
| P210, P235+410, P240, P241, P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P330, P363, P370+378, P405, P407, P413, P420, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
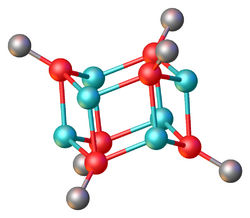
Lithium tert-butoxide is the metalorganic compound with the formula LiOC(CH3)3. A white solid, it is used as a strong base in organic synthesis. The compound is often depicted as a salt, and it often behaves as such, but it is not ionized in solution. Both octameric[1] and hexameric forms have been characterized by X-ray crystallography[2]
Preparation
Lithium tert-butoxide is commercially available as a solution and as a solid, but it is often generated in situ for laboratory use because samples are so sensitive and older samples are often of poor quality. It can be obtained by treating tert-butanol with butyl lithium.[3]
Reactions
As a strong base, lithium tert-butoxide is easily protonated.
Lithium tert-butoxide is used to prepare other tert-butoxide compounds such as copper(I) t-butoxide and hexa(tert-butoxy)dimolybdenum(III):[4]
- 2 MoCl3(thf)3 + 6 LiOBu-t → Mo2(OBu-t)6 + 6 LiCl + 6 thf
Related compounds
References
- ↑ Nekola, Henning; Olbrich, Falk; Behrens, Ulrich (2002). "Kristall- und Molekülstrukturen von Lithium- und Natrium-tert-butoxid". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 628 (9–10): 2067–2070. doi:10.1002/1521-3749(200209)628:9/10<2067::AID-ZAAC2067>3.0.CO;2-N.
- ↑ Allan, John F.; Nassar, Roger; Specht, Elizabeth; Beatty, Alicia; Calin, Nathalie; Henderson, Kenneth W. (2004). "Characterization of a Kinetically Stable, Highly Ordered, Octameric Form of Lithiumtert-Butoxide and Its Implications Regarding Aggregate Formation". Journal of the American Chemical Society 126 (2): 484–485. doi:10.1021/ja038420m. PMID 14719943.
- ↑ Crowther, G. P.; Kaiser, E. M.; Woodruff, R. A.; Hauser, C. R. (1971). "Esterification Of Hindered Alcohols: tert-Butyl p-Toluate". Organic Syntheses 51: 96. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.051.0096.
- ↑ Broderick, Erin M.; Browne, Samuel C.; Johnson, Marc J. A. (2014). Dimolybdenum and Ditungsten Hexa(Alkoxides). Inorganic Syntheses. 36. pp. 95–102. doi:10.1002/9781118744994.ch18. ISBN 9781118744994.
 |