Chemistry:Nemonoxacin
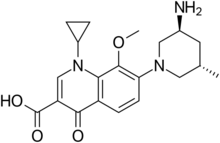
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
7-[(3S,5S)-3-Amino-5-methylpiperidin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H25N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 371.437 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | J01MB08 (WHO) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Nemonoxacin is a non-fluorinated quinolone antibiotic undergoing clinical trials.[1] It has the same mechanism of action as fluouroquinolones; it inhibits DNA gyrase, preventing DNA synthesis, gene duplication, and cell division. At the end of 2016, it had reached market in Taiwan, Russia, the Commonwealth Independent States, Turkey, mainland China,[2] and Latin America[3] under the brand name Taigexyn. Nemonoxacin has completed phase 2 trials in the US and has moved on to phase 3 trials.[4] The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted nemonoxacin qualified infectious disease product (QIDP) and fast track designations for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CAP) and acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections (ABSSSI).[5]
Nemonoxacin has a broad spectrum of activity against Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and atypical pathogens, including activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (MIC90 1 g/ml) and vancomycin-resistant pathogens.[6][7] However, it was less active against Gram-negative pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with MIC90 values of 32, 16, and 32 g/ml, respectively.[8] The new drug also is effective against C.difficile isolates that are resistant to other quinolones,[9] and is more potent than levofloxacin or moxifloxacin.[10]
References
- ↑ Guo, B; Wu, X; Zhang, Y; Shi, Y; Yu, J; Cao, G; Zhang, J (2012). "Safety and clinical pharmacokinetics of nemonoxacin, a novel non-fluorinated quinolone, in healthy Chinese volunteers following single and multiple oral doses". Clinical Drug Investigation 32 (7): 475–86. doi:10.2165/11632780-000000000-00000. PMID 22650326.
- ↑ "TaiGen releases Taigexyn (nemonoxacin) capsules in Taiwan". 16 December 2015. http://www.news-medical.net/news/20151216/TaiGen-releases-Taigexyn-(nemonoxacin)-capsules-in-Taiwan.aspx.
- ↑ Biotechnology, TaiGen. "TaiGen Biotechnology Out-Licenses Taigexyn® (Nemonoxacin) to Productos Científicos for the Latin American Market" (Press release).
- ↑ "A Phase III Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Infusion of Nemonoxacin in Treating CAP - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov". https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02205112.
- ↑ "FDA grants QIDP and Fast Track designations to TaiGen's nemonoxacin". 23 December 2013. http://www.news-medical.net/news/20131223/FDA-grants-QIDP-and-Fast-Track-designations-to-TaiGens-nemonoxacin.aspx.
- ↑ "Comparative in vitro activities of nemonoxacin (TG-873870), a novel nonfluorinated quinolone, and other quinolones against clinical isolates". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 (3): 1338–1342. 2010. doi:10.1128/aac.01197-09. PMID 20065058.
- ↑ "In vitro activity of nemonoxacin, a novel nonfluorinated quinolone, against 2,440 clinical isolates". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 (11): 4915–4920. 2009. doi:10.1128/aac.00078-09. PMID 19738018.
- ↑ "Efficacy and safety of nemonoxacin versus levofloxacin for community-acquired pneumonia". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 (10): 4098–4106. 2010. doi:10.1128/aac.00295-10. PMID 20660689.
- ↑ Liao, C. H.; Ko, W. C.; Lu, J. J.; Hsueh, P. R. (2012). "Characterizations of Clinical Isolates of Clostridium difficile by Toxin Genotypes and by Susceptibility to 12 Antimicrobial Agents, Including Fidaxomicin (OPT-80) and Rifaximin: A Multicenter Study in Taiwan". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 56 (7): 3943–3949. doi:10.1128/AAC.00191-12. PMID 22508299.
- ↑ Liang, W; Chen, Y. C.; Cao, Y. R.; Liu, X. F.; Huang, J; Hu, J. L.; Zhao, M; Guo, Q. L. et al. (2013). "Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nemonoxacin against Streptococcus pneumoniae in an in Vitro Infection Model". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (7): 2942–2947. doi:10.1128/AAC.01098-12. PMID 23587953.
 |
