Biology:Furazolidone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral-Local |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
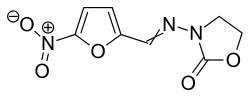
| Formula | C8H7N3O5 |
| Molar mass | 225.16 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Furazolidone is a nitrofuran antibacterial agent and monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).[1] It is marketed by Roberts Laboratories under the brand name Furoxone and by GlaxoSmithKline as Dependal-M.
Medical uses
Furazolidone has been used in human and veterinary medicine. It has a broad spectrum of activity being active against[citation needed]
- Gram positivei
- Clostridium perfringens
- Corynebacterium pyogenes
- Streptococci
- Staphylococci
- Gram negative
- Escherichia coli
- Salmonella dublin
- Salmonella typhimurium
- Shigella
- Protozoa
- Giardia lamblia
- Eimeria species
- Histomonas meleagridis
Use in humans
In humans it has been used to treat diarrhoea and enteritis caused by bacteria or protozoan infections, including traveler's diarrhoea, cholera and bacteremic salmonellosis.
From the early 1970s it has been used in China to treat peptic ulcers, where the mechanism is treatment of the causative Helicobacter pylori infection.[2] In 2002, a journal article suggested its use in treatment of helicobacter pylori infections in children.[3]
Furazolidone has also been used for giardiasis (due to Giardia lamblia), amoebiasis and shigellosis also though it is not a first line treatment.[4]
Use in animals
As a veterinary medicine, furazolidone has been used with some success to treat salmonids for Myxobolus cerebralis infections.[citation needed]
It has also been used in aquaculture.[5]
Since furazolidone is a nitrofuran antibiotic, its use in food animals is currently prohibited by the FDA under the Animal Medicinal Drug Use Clarification Act, 1994.[6]
Furazolidone is no longer available in the US.[citation needed]
Use in laboratory
It is used to differentiate micrococci and staphylococci.[citation needed]
Mechanism of action
It is believed to work by crosslinking of DNA.[7]
Side effects
Though an effective antibiotic when all others fail, against extremely drug resistant infections, it has many side effects. including inhibition of monoamine oxidase,[1] and as with other nitrofurans generally, minimum inhibitory concentrations also produce systemic toxicity: tremors, convulsions, peripheral neuritis, gastrointestinal disturbances, depression of spermatogenesis. Nitrofurans are recognized by FDA as mutagens/carcinogens, and can no longer be used since 1991.[8]
See also
- Nitrofurazone
- Nitrofurantoin
- Norwich Pharmacal Co. & Others v Customs and Excise Commissioners
- Peptic ulcers and Helicobacter pylori
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Identification of a furazolidone metabolite responsible for the inhibition of amino oxidases". Xenobiotica; the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems 33 (2): 153–167. February 2003. doi:10.1080/0049825021000038459. PMID 12623758.
- ↑ "How we discovered in Cina in 1972 that antibiotics cure peptic ulcer.". Helicobacter Pioneers: Firsthand Accounts from the Scientists Who Discovered Helicobacters, 1893-1983. Wiley. 2002. pp. 99–104. ISBN 978-0-86793-035-1.
- ↑ "Furazolidone, tetracycline and omeprazole: a low-cost alternative for Helicobacter pylori eradication in children". Jornal de Pediatria 84 (2): 160–165. 2008. doi:10.2223/JPED.1772. PMID 18372934.
- ↑ "Treatment of Giardiasis". Current Treatment Options in Gastroenterology 8 (1): 13–17. February 2005. doi:10.1007/s11938-005-0047-3. PMID 15625030.
- ↑ "Evidence of 14C-furazolidone metabolite binding to the hepatic DNA of trout". Drug Metabolism and Drug Interactions 14 (4): 209–219. 1998. doi:10.1515/DMDI.1998.14.4.209. PMID 10694929.
- ↑ "Drugs Prohibited from Extralabel Use in Animals". Utah State University Extension. http://extension.usu.edu/dairy/files/uploads/htms/drugs.htm.
- ↑ "Furazolidone (DB00614)". DrugBank. http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00614.
- ↑ "Declaring a Ban/Phase-Out of the Use of Nitrofurans in Food-Producing Animals.". Department of Health, Department of Agriculture. Republic of the Philippines. 17 August 2000. http://caraga.da.gov.ph/services/banmed-Nitrofurans.htm.
 |

