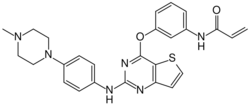
Chemistry:Olmutinib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | HM-61713, BI-1482694 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H26N6O2S |
| Molar mass | 486.59 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Olmutinib (INN)[1] is an investigational anti-cancer drug. It acts by covalently bonding to a cysteine residue near the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).[2]
In the US, it was given a breakthrough therapy designation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in December 2015, and In South Korea, the drug was approved in May 2016 for the second-line treatment of NSCLC with the T790M mutation of EGFR.[2] Resistance to olmutinib has been reported; a person's cancer started progressing after they developed a C797S mutation in EGFR.[2][3]
Olmutinib was discovered by Hanmi Pharmaceutical and licensed to Boehringer Ingelheim in 2015 in an agreement with a $50 million up front payment and up $680 million in milestones.[4] In November 2015 Hanmi granted an exclusive license to sell olmutinib in China to the Chinese company ZAI Labs.[5]
On September 30, 2016, Korean regulatory authorities issued a safety alert about olmutinib in which it described two cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, one of which was fatal, and a case of Stevens–Johnson syndrome; Boeheringer announced the termination its deal with Hanmi the same day, citing that the decision came after a review of "all available clinical data" on the drug, and also referring to competing drugs.[6]
References
- ↑ "Olmutinib" (in en). AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800036204.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Update on recent preclinical and clinical studies of T790M mutant-specific irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors". Journal of Biomedical Science 23 (1): 86. December 2016. doi:10.1186/s12929-016-0305-9. PMID 27912760.
- ↑ "Targeting EGFR T790M mutation in NSCLC: From biology to evaluation and treatment". Pharmacological Research 117: 406–415. March 2017. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2017.01.003. PMID 28089942.
- ↑ Garde, Damian (July 29, 2015). "Boehringer bets up to $730M on a new lung cancer drug" (in en). FierceBiotech. http://www.fiercebiotech.com/partnering/boehringer-bets-up-to-730m-on-a-new-lung-cancer-drug.
- ↑ Keenan, Joseph (April 14, 2016). "South Korea's Hanmi to spend $200M in China expansion" (in en). FiercePharma. http://www.fiercepharma.com/manufacturing/south-korea-s-hanmi-to-spend-200m-china-expansion.
- ↑ Carroll, John (October 1, 2016). "Following lethal tox report, Boehringer scraps plans for high-speed development, kills $730M Hanmi deal". Endpoints. https://endpts.com/following-lethal-tox-report-boehringer-scraps-plans-for-high-speed-development-kills-730m-hanmi-deal/.
 |
