Medicine:Pipecolic acidemia
From HandWiki
| Pipecolic acidemia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hyperpipecolic acidemia or Hyperpipecolatemia[1] |
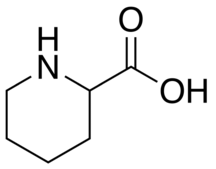 | |
| Pipecolic acid | |
Pipecolic acidemia is a very rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that is caused by a peroxisomal defect.
Pipecolic acidemia can also be an associated component of Refsum disease with increased pipecolic acidemia (RDPA),[2] as well as other peroxisomal disorders, including both infantile and adult Refsum disease,[3][4][5] and Zellweger syndrome.[6]
The disorder is characterized by an increase in pipecolic acid levels in the blood, leading to neuropathy and hepatomegaly.[citation needed]
See also
- AASDHPPT
- PHYH
References
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 239400
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 600964
- ↑ "A new peroxisomal disease with impaired phytanic and pipecolic acid oxidation". Neurology 43 (10): 2044–2048. Oct 1993. doi:10.1212/wnl.43.10.2044. PMID 8413964.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 266510
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 266500
- ↑ Brul, S.; Westerveld, A.; Strijland, A.; Wanders, R.; Schram, A.; Heymans, H.; Schutgens, R.; Van Den Bosch, H. et al. (June 1988). "Genetic heterogeneity in the cerebrohepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome and other inherited disorders with a generalized impairment of peroxisomal functions. A study using complementation analysis". Journal of Clinical Investigation 81 (6): 1710–1715. doi:10.1172/JCI113510. PMID 2454948.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
 |
