Chemistry:Martin's sulfurane
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bis[(1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-phenylpropan-2-yl)oxy]diphenyl-λ4-sulfane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H20F12O2S | |
| Molar mass | 672.53 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 107–109 °C (225–228 °F; 380–382 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
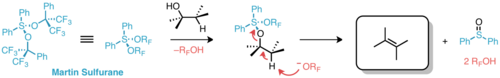
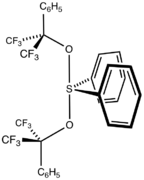
Martin's sulfurane is the organosulfur compound with the formula Ph2S[OC(CF3)2Ph]2 (Ph = C6H5). It is a white solid that easily undergoes sublimation. The compound is an example of a hypervalent sulfur compound called a sulfurane. As such, the sulfur adopts a see-saw structure, with a lone pair of electrons as the equatorial fifth coordinate of a trigonal bipyramid, like that of sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4).[1] The compound is a reagent in organic synthesis. One application is for the dehydration of a secondary alcohol to give an alkene:[2]
- RCH(OH)CH2R' + Ph2S[OC(CF3)2Ph]2 → RCH=CHR' + Ph2SO + 2 HOC(CF3)2Ph
References
- ↑ Martin, J. C.; Arhart, R. J.; Franz, J. A.; Perozzi, E. F.; Kaplan, L. J.. "Bis[2,2,2-trifluoro-1-phenyl-1-(trifluoromethyl)ethoxy]diphenyl sulfurane". Organic Syntheses 57: 22. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.057.0022.
- ↑ Roden, Brian A. (2001). "Diphenylbis(1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-phenyl-2-propoxy)sulfurane". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd409. ISBN 0471936235.
 |