Chemistry:Methyl thiocyanate
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl thiocyanate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | C047435 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2929 1935 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3NS | |
| Molar mass | 73.117 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.074 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −51 °C (−60 °F; 222 K) |
| Boiling point | 132 °C (270 °F; 405 K) (101.3 kP) |
| Slightly soluble[3] | |
| Solubility in Diethyl ether | Miscible[3] |
| Structure | |
| bent C-S-CN | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H301, H311, H315, H319, H330, H331, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+310, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P311, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 38 °C (100 °F; 311 K)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Methyl isocyanate Methyl isothiocyanate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
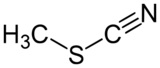
Methyl thiocyanate is an organic compound with the formula CH3SCN. The simplest member of the organic thiocyanates, it is a colourless liquid with an onion-like odor. It is produced by the methylation of thiocyanate salts. The compound is a precursor to the more useful isomer methyl isothiocyanate (CH3NCS).[4]
Safety
The LD50 is 60 mg/kg (rats, oral).
It is listed as an extremely hazardous substance by the United States 's Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Chemblink chemical data". http://www.chemblink.com/products/556-64-9.htm. Retrieved June 29, 2011.
- ↑ "Chemical book page". http://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB8853822.htm. Retrieved June 29, 2011.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "United States chemical entree". http://www.osha.gov/dts/chemicalsampling/data/CH_254775.html. Retrieved June 29, 2011.
- ↑ F. Romanowski, H. Klenk "Thiocyanates and Isothiocyanates, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_749
- ↑ 40 C.F.R.: Appendix A to Part 355—The List of Extremely Hazardous Substances and Their Threshold Planning Quantities (July 1, 2008 ed.), Government Printing Office, http://edocket.access.gpo.gov/cfr_2008/julqtr/pdf/40cfr355AppA.pdf, retrieved March 8, 2009
 |


