Chemistry:FGI-106
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
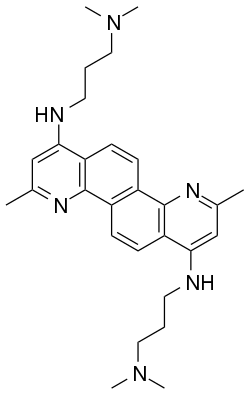 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H38N6 |
| Molar mass | 458.654 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
FGI-106 is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug developed as a potential treatment for enveloped RNA viruses, in particular viral hemorrhagic fevers from the bunyavirus, flavivirus and filovirus families. It acts as an inhibitor which blocks viral entry into host cells. In animal tests FGI-106 shows both prophylactic and curative action against a range of deadly viruses for which few existing treatments are available, including the bunyaviruses hantavirus, Rift Valley fever virus and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, the flavivirus dengue virus, and the filoviruses Ebola virus and Marburg virus.[1][2][3][4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ "Development of a broad-spectrum antiviral with activity against Ebola virus". Antiviral Research 83 (3): 245–51. September 2009. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.06.001. PMID 19523489.
- ↑ "Development of FGI-106 as a broad-spectrum therapeutic with activity against members of the family Bunyaviridae". Virus Adaptation and Treatment: 9. 2010. doi:10.2147/VAAT.S6903.
- ↑ "Identification of a small-molecule entry inhibitor for filoviruses". Journal of Virology 85 (7): 3106–19. April 2011. doi:10.1128/JVI.01456-10. PMID 21270170.
- ↑ "Viral hemorrhagic fevers: advancing the level of treatment". BMC Medicine 10: 31. March 2012. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-10-31. PMID 22458265.
- ↑ "Small molecule inhibitors of ebola virus infection". Drug Discovery Today 20 (2): 277–86. February 2015. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2014.12.010. PMID 25532798.
 |

