Astronomy:TU Andromedae
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Andromeda |
| Right ascension | 00h 32m 22.72867s[2] |
| Declination | +26° 01′ 45.9211″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.5 – 13.5[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M5e[3] |
| B−V color index | 0.96[4] |
| Variable type | Mira[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −7.435±0.069[2] mas/yr Dec.: −3.136±0.057[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.9435 ± 0.0623[2] mas |
| Distance | 3,500 ± 200 ly (1,060 ± 70 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.87[5] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 5,200 - 5,400[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | −0.44[5] cgs |
| Temperature | 2,639[5] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.547[5] dex |
| Other designations | |
HD 2890, HIP 2546, 2MASS J00322275+2601459 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
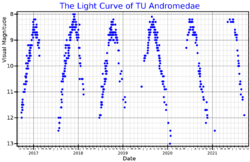
TU Andromedae (TU And) is a variable star of the Mira type in the constellation Andromeda. It has a spectral type of M5e and a visual magnitude which varies between extremes of 7.6 and 13.5.
Like all the stars of this kind, TU And is a cool asymptotic giant branch star, meaning it is fusing hydrogen and helium in concentric shells outside an inert core of carbon and oxygen formed earlier in its life on the horizontal branch. Its period is stable at 316.8 days.[3]
The modelled properties of TU Andromedae at maximum brightness are not in agreement with available models of Mira stars (which work for Mira itself). It is uncertain if the problem is in the measured parameters of the star or in imperfections of the models. It had a mass between 1.15 and 1.4 M☉ when it was on the main sequence but is now less massive.[6]
References
- ↑ "Download Data". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/data-download.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 TU And, database entry, Combined General Catalog of Variable Stars (GCVS4.2, 2004 Ed.), N. N. Samus, O. V. Durlevich, et al., CDS ID II/250 Accessed on line 2009-06-30.
- ↑ Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P. et al. (2000), "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars", Astronomy & Astrophysics 355: L27–L30, Bibcode: 2000A&A...355L..27H.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Anders, F.; Khalatyan, A.; Chiappini, C.; Queiroz, A. B.; Santiago, B. X.; Jordi, C.; Girardi, L.; Brown, A. G. A. et al. (2019), "Photo-astrometric distances, extinctions, and astrophysical parameters for Gaia DR2 stars brighter than G = 18", Astronomy and Astrophysics 628: A94, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935765, Bibcode: 2019A&A...628A..94A.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Hillen, M.; Verhoelst, T.; Degroote, P.; Acke, B.; van Winckel, H. (2012), "The dynamic atmospheres of Mira stars: comparing the CODEX models to PTI time series of TU Andromedae", Astronomy & Astrophysics 538: L6, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201118653, Bibcode: 2012A&A...538L...6H.
 |