Astronomy:IC 5146
| Reflection nebula | |
|---|---|
| emission nebula | |
 Optical image of IC 5146 | |
| Observation data: J2000 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 21h 53m 28.7s |
| Declination | +47° 16′ 01″ |
| Distance | 2500±100[1] ly (780±30 pc) |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +7.2 |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 12′ |
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Radius | 7.5 ly |
| Designations | Cocoon Nebula, Caldwell 19, Sh 2-125, Cr 470 |
IC 5146 (also Caldwell 19, Sh 2-125, Barnard 168, and the Cocoon Nebula) is a reflection[2]/emission[3] nebula and Caldwell object in the constellation Cygnus. The NGC description refers to IC 5146 as a cluster of 9.5 mag stars involved in a bright and dark nebula. The cluster is also known as Collinder 470.[4] It shines at magnitude +10.0[5]/+9.3[3]/+7.2.[6] Its celestial coordinates are RA 21h 53.5m, dec +47° 16′. It is located near the naked-eye star Pi Cygni, the open cluster NGC 7209 in Lacerta, and the bright open cluster M39.[2][5] The cluster is about 4,000 ly away, and the central star that lights it formed about 100,000 years ago;[7] the nebula is about 12 arcmins across, which is equivalent to a span of 15 light years.[6]
When viewing IC 5146, dark nebula Barnard 168 (B168) is an inseparable part of the experience, forming a dark lane that surrounds the cluster and projects westward forming the appearance of a trail behind the Cocoon.
Young Stellar Objects
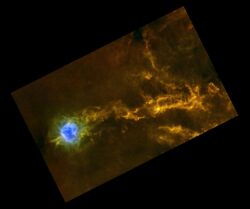
IC 5146 is a stellar nursery where star-formation is ongoing. Observations by both the Spitzer Space Telescope and the Chandra X-ray Observatory have collectively identified hundreds of young stellar objects.[8][9] Young stars are seen in both the emission nebula, where gas has been ionized by massive young stars, and in the infrared-dark molecular cloud that forms the "tail". One of the most massive stars in the region is BD +46 3474, a star of class B1 that is an estimated 14±4 times the mass of the sun.[10]
Another interesting star in the nebula is BD +46 3471, which is an example of a HAeBe star, an intermediate mass star with strong emission lines in its spectrum.[11]
References
- ↑ Kuhn, Michael A.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A.; Sills, Alison; Feigelson, Eric D.; Getman, Konstantin V. (2018). "Kinematics in Young Star Clusters and Associations with Gaia DR2". The Astrophysical Journal 870 (1): 32. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aaef8c. Bibcode: 2019ApJ...870...32K.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Eicher, David J. (1988). The Universe from Your Backyard: A Guide to Deep-Sky Objects from Astronomy Magazine. AstroMedia (Kalmbach Publishing Company). ISBN 0-521-36299-7. https://archive.org/details/universefromyour0000eich.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Sanqunetti, Doug (2007). "IC 5146 - Cocoon Nebula". dougsastro.net. http://dougsastro.net/IC-Catalog/ic5146.php.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ O'Meara, Stephen James: The Caldwell Objects, Sky Publishing Corporation ISBN 0-933346-97-2 page 80
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Pasachoff, Jay M. (2000). "Atlas of the Sky". Stars and Planets. New York, NY: Peterson Field Guides. pp. 578. ISBN 0-395-93432-X.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Cannistra, Steve (2004). "Cocoon Nebula". starrywonders.com. http://www.starrywonders.com/cocoon.html.
- ↑ Nemiroff, R.; Bonnell, J., eds (2002-10-14). "IC 5146: The Cocoon Nebula". Astronomy Picture of the Day. NASA. https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap021014.html.
- ↑ Harvey, Paul M.; Huard, Tracy L.; Jørgensen, Jes K.; Gutermuth, Robert A.; Mamajek, Eric E.; Bourke, Tyler L.; Merín, Bruno; Cieza, Lucas et al. (2008). "TheSpitzerSurvey of Interstellar Clouds in the Gould Belt. I. IC 5146 Observed With IRAC and MIPS". The Astrophysical Journal 680 (1): 495–516. doi:10.1086/587687. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 2008ApJ...680..495H.
- ↑ Getman, Konstantin V.; Broos, Patrick S.; Kuhn, Michael A.; Feigelson, Eric D.; Richert, Alexander J. W.; Ota, Yosuke; Bate, Matthew R.; Garmire, Gordon P. (2017). "Star Formation In Nearby Clouds (SFiNCs): X-Ray and Infrared Source Catalogs and Membership". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 229 (2): 28. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/229/2/28. ISSN 1538-4365. Bibcode: 2017ApJS..229...28G.
- ↑ Weidner, Carsten; Kroupa, Pavel (2006). "The maximum stellar mass, star-cluster formation and composite stellar populations". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 365 (4): 1333–1347. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09824.x. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2006MNRAS.365.1333W.
- ↑ Reipurth, Bo (2008). Handbook of star forming regions. San Francisco: Astronomical Society of the Pacific. ISBN 978-1-58381-670-7.
External links
- "IC 5146". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=IC+5146.
- "NED results for object IC 5146". NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. National Aeronautics and Space Administration / Infrared Processing and Analysis Center. http://nedwww.ipac.caltech.edu/cgi-bin/nph-objsearch?objname=IC+5146&extend=no&out_csys=Equatorial&out_equinox=J2000.0&obj_sort=RA+or+Longitude&of=pre_text&zv_breaker=30000.0&list_limit=5&img_stamp=YES.
- IC 5146 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
Coordinates: ![]() 21h 53m 32s, +47° 16′ 06″
21h 53m 32s, +47° 16′ 06″
 |
