Physics:Toric code
The toric code is a topological quantum error correcting code, and an example of a stabilizer code, defined on a two-dimensional spin lattice.[1] It is the simplest and most well studied of the quantum double models.[2] It is also the simplest example of topological order—Z2 topological order (first studied in the context of Z2 spin liquid in 1991).[3][4] The toric code can also be considered to be a Z2 lattice gauge theory in a particular limit.[5] It was introduced by Alexei Kitaev.
The toric code gets its name from its periodic boundary conditions, giving it the shape of a torus. These conditions give the model translational invariance, which is useful for analytic study. However, some experimental realizations require open boundary conditions, allowing the system to be embedded on a 2D surface. The resulting code is typically known as the planar code. This has identical behaviour to the toric code in most, but not all, cases.
Error correction and computation
The toric code is defined on a two-dimensional lattice, usually chosen to be the square lattice, with a spin-½ degree of freedom located on each edge. They are chosen to be periodic. Stabilizer operators are defined on the spins around each vertex and plaquette[definition needed] (or face i.e. a vertex of the dual lattice)[clarification needed] of the lattice as follows,
Where here we use to denote the edges touching the vertex , and to denote the edges surrounding the plaquette . The stabilizer space of the code is that for which all stabilizers act trivially, hence for any state in this space it holds that
For the toric code, this space is four-dimensional, and so can be used to store two qubits of quantum information. This can be proven by considering the number of independent stabilizer operators. The occurrence of errors will move the state out of the stabilizer space, resulting in vertices and plaquettes for which the above condition does not hold. The positions of these violations is the syndrome of the code, which can be used for error correction.
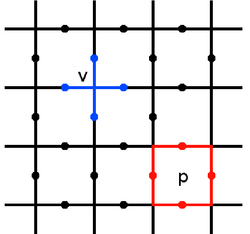
The unique nature of the topological codes, such as the toric code, is that stabilizer violations can be interpreted as quasiparticles. Specifically, if the code is in a state such that,
,
a quasiparticle known as an anyon can be said to exist on the vertex . Similarly violations of the are associated with so called anyons on the plaquettes. The stabilizer space therefore corresponds to the anyonic vacuum. Single spin errors cause pairs of anyons to be created and transported around the lattice.
When errors create an anyon pair and move the anyons, one can imagine a path connecting the two composed of all links acted upon. If the anyons then meet and are annihilated, this path describes a loop. If the loop is topologically trivial, it has no effect on the stored information. The annihilation of the anyons, in this case, corrects all of the errors involved in their creation and transport. However, if the loop is topologically non-trivial, though re-annihilation of the anyons returns the state to the stabilizer space, it also implements a logical operation on the stored information. The errors, in this case, are therefore not corrected but consolidated.
Consider the noise model for which bit and phase errors occur independently on each spin, both with probability p. When p is low, this will create sparsely distributed pairs of anyons which have not moved far from their point of creation. Correction can be achieved by identifying the pairs that the anyons were created in (up to an equivalence class), and then re-annihilating them to remove the errors. As p increases, however, it becomes more ambiguous as to how the anyons may be paired without risking the formation of topologically non-trivial loops. This gives a threshold probability, under which the error correction will almost certainly succeed. Through a mapping to the random-bond Ising model, this critical probability has been found to be around 11%.[6]
Other error models may also be considered, and thresholds found. In all cases studied so far, the code has been found to saturate the Hashing bound. For some error models, such as biased errors where bit errors occur more often than phase errors or vice versa, lattices other than the square lattice must be used to achieve the optimal thresholds.[7][8]
These thresholds are upper limits and are useless unless efficient algorithms are found to achieve them. The most well-used algorithm is minimum weight perfect matching.[9] When applied to the noise model with independent bit and flip errors, a threshold of around 10.5% is achieved. This falls only a little short of the 11% maximum. However, matching does not work so well when there are correlations between the bit and phase errors, such as with depolarizing noise.
The means to perform quantum computation on logical information stored within the toric code has been considered, with the properties of the code providing fault-tolerance. It has been shown that extending the stabilizer space using 'holes', vertices or plaquettes on which stabilizers are not enforced, allows many qubits to be encoded into the code. However, a universal set of unitary gates cannot be fault-tolerantly implemented by unitary operations and so additional techniques are required to achieve quantum computing. For example, universal quantum computing can be achieved by preparing magic states via encoded quantum stubs called tidBits used to teleport in the required additional gates when replaced as a qubit. Furthermore, preparation of magic states must be fault tolerant, which can be achieved by magic state distillation on noisy magic states. A measurement based scheme for quantum computation based upon this principle has been found, whose error threshold is the highest known for a two-dimensional architecture.[10][11]
Hamiltonian and self-correction
Since the stabilizer operators of the toric code are quasilocal, acting only on spins located near each other on a two-dimensional lattice, it is not unrealistic to define the following Hamiltonian,
The ground state space of this Hamiltonian is the stabilizer space of the code. Excited states correspond to those of anyons, with the energy proportional to their number. Local errors are therefore energetically suppressed by the gap, which has been shown to be stable against local perturbations.[12] However, the dynamic effects of such perturbations can still cause problems for the code.[13][14]
The gap also gives the code a certain resilience against thermal errors, allowing it to be correctable almost surely for a certain critical time. This time increases with , but since arbitrary increases of this coupling are unrealistic, the protection given by the Hamiltonian still has its limits.
The means to make the toric code, or the planar code, into a fully self-correcting quantum memory is often considered. Self-correction means that the Hamiltonian will naturally suppress errors indefinitely, leading to a lifetime that diverges in the thermodynamic limit. It has been found that this is possible in the toric code only if long range interactions are present between anyons.[15][16] Proposals have been made for realization of these in the lab [17] Another approach is the generalization of the model to higher dimensions, with self-correction possible in 4D with only quasi-local interactions.[18]
Anyon model
As mentioned above, so called and quasiparticles are associated with the vertices and plaquettes of the model, respectively. These quasiparticles can be described as anyons, due to the non-trivial effect of their braiding. Specifically, though both species of anyons are bosonic with respect to themselves, the braiding of two 's or 's having no effect, a full monodromy of an and an will yield a phase of . Such a result is not consistent with either bosonic or fermionic statistics, and hence is anyonic.
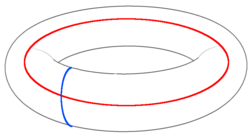
The anyonic mutual statistics of the quasiparticles demonstrate the logical operations performed by topologically non-trivial loops. Consider the creation of a pair of anyons followed by the transport of one around a topologically nontrivial loop, such as that shown on the torus in blue on the figure above, before the pair are reannhilated. The state is returned to the stabilizer space, but the loop implements a logical operation on one of the stored qubits. If anyons are similarly moved through the red loop above a logical operation will also result. The phase of resulting when braiding the anyons shows that these operations do not commute, but rather anticommute. They may therefore be interpreted as logical and Pauli operators on one of the stored qubits. The corresponding logical Pauli's on the other qubit correspond to an anyon following the blue loop and an anyon following the red. No braiding occurs when and pass through parallel paths, the phase of therefore does not arise and the corresponding logical operations commute. This is as should be expected since these form operations acting on different qubits.
Due to the fact that both and anyons can be created in pairs, it is clear to see that both these quasiparticles are their own antiparticles. A composite particle composed of two anyons is therefore equivalent to the vacuum, since the vacuum can yield such a pair and such a pair will annihilate to the vacuum. Accordingly, these composites have bosonic statistics, since their braiding is always completely trivial. A composite of two anyons is similarly equivalent to the vacuum. The creation of such composites is known as the fusion of anyons, and the results can be written in terms of fusion rules. In this case, these take the form,
Where denotes the vacuum. A composite of an and an is not trivial. This therefore constitutes another quasiparticle in the model, sometimes denoted , with fusion rule,
From the braiding statistics of the anyons we see that, since any single exchange of two 's will involve a full monodromy of a constituent and , a phase of will result. This implies fermionic self-statistics for the 's.
Generalizations
The use of a torus is not required to form an error correcting code. Other surfaces may also be used, with their topological properties determining the degeneracy of the stabilizer space. In general, quantum error correcting codes defined on two-dimensional spin lattices according to the principles above are known as surface codes.[19]
It is also possible to define similar codes using higher-dimensional spins. These are the quantum double models[20] and string-net models,[21] which allow a greater richness in the behaviour of anyons, and so may be used for more advanced quantum computation and error correction proposals.[22] These not only include models with Abelian anyons, but also those with non-Abelian statistics.[23][24][25]
Experimental progress
The most explicit demonstration of the properties of the toric code has been in state based approaches. Rather than attempting to realize the Hamiltonian, these simply prepare the code in the stabilizer space. Using this technique, experiments have been able to demonstrate the creation, transport and statistics of the anyons[26][27][28] and measurement of the topological entanglement entropy.[28] More recent experiments have also been able to demonstrate the error correction properties of the code.[29][28]
For realizations of the toric code and its generalizations with a Hamiltonian, much progress has been made using Josephson junctions. The theory of how the Hamiltonians may be implemented has been developed for a wide class of topological codes.[30] An experiment has also been performed, realizing the toric code Hamiltonian for a small lattice, and demonstrating the quantum memory provided by its degenerate ground state.[31]
Other theoretical and experimental works towards realizations are based on cold atoms. A toolkit of methods that may be used to realize topological codes with optical lattices has been explored, [32] as have experiments concerning minimal instances of topological order.[33] Such minimal instances of the toric code has been realized experimentally within isolated square plaquettes.[34] Progress is also being made into simulations of the toric model with Rydberg atoms, in which the Hamiltonian and the effects of dissipative noise can be demonstrated.[35][36] Experiments in Rydberg atom arrays have also successfully realized the toric code with periodic boundary conditions in two dimensions by coherently transporting arrays of entangled atoms.[37]
References
- ↑ A. Y. Kitaev, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Quantum Communication and Measurement, Ed. O. Hirota, A. S. Holevo, and C. M. Caves (New York, Plenum, 1997)
- ↑ Kitaev, Alexei (2006). "Anyons in an exactly solved model and beyond". Annals of Physics 321 (1): 2–111. doi:10.1016/j.aop.2005.10.005. ISSN 0003-4916. Bibcode: 2006AnPhy.321....2K.
- ↑ Read, N.; Sachdev, Subir (1 March 1991). "Large-Nexpansion for frustrated quantum antiferromagnets". Physical Review Letters 66 (13): 1773–1776. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.66.1773. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 10043303. Bibcode: 1991PhRvL..66.1773R.
- ↑ Wen, X. G. (1 July 1991). "Mean-field theory of spin-liquid states with finite energy gap and topological orders". Physical Review B 44 (6): 2664–2672. doi:10.1103/physrevb.44.2664. ISSN 0163-1829. PMID 9999836. Bibcode: 1991PhRvB..44.2664W.
- ↑ Fradkin, Eduardo; Shenker, Stephen H. (15 June 1979). "Phase diagrams of lattice gauge theories with Higgs fields". Physical Review D 19 (12): 3682–3697. doi:10.1103/physrevd.19.3682. ISSN 0556-2821. Bibcode: 1979PhRvD..19.3682F.
- ↑ Dennis, Eric; Kitaev, Alexei; Landahl, Andrew; Preskill, John (2002). "Topological quantum memory". Journal of Mathematical Physics 43 (9): 4452–4505. doi:10.1063/1.1499754. ISSN 0022-2488. Bibcode: 2002JMP....43.4452D.
- ↑ Röthlisberger, Beat; Wootton, James R.; Heath, Robert M.; Pachos, Jiannis K.; Loss, Daniel (13 February 2012). "Incoherent dynamics in the toric code subject to disorder". Physical Review A 85 (2): 022313. doi:10.1103/physreva.85.022313. ISSN 1050-2947. Bibcode: 2012PhRvA..85b2313R.
- ↑ Bombin, H.; Andrist, Ruben S.; Ohzeki, Masayuki; Katzgraber, Helmut G.; Martin-Delgado, M. A. (30 April 2012). "Strong Resilience of Topological Codes to Depolarization". Physical Review X 2 (2): 021004. doi:10.1103/physrevx.2.021004. ISSN 2160-3308. Bibcode: 2012PhRvX...2b1004B.
- ↑ Edmonds, Jack (1965). "Paths, Trees, and Flowers". Canadian Journal of Mathematics 17: 449–467. doi:10.4153/cjm-1965-045-4. ISSN 0008-414X.
- ↑ Raussendorf, Robert; Harrington, Jim (11 May 2007). "Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation with High Threshold in Two Dimensions". Physical Review Letters 98 (19): 190504. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.98.190504. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 17677613. Bibcode: 2007PhRvL..98s0504R.
- ↑ Raussendorf, R; Harrington, J; Goyal, K (29 June 2007). "Topological fault-tolerance in cluster state quantum computation". New Journal of Physics 9 (6): 199. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/9/6/199. ISSN 1367-2630. Bibcode: 2007NJPh....9..199R.
- ↑ Bravyi, Sergey; Hastings, Matthew B.; Michalakis, Spyridon (2010). "Topological quantum order: Stability under local perturbations". Journal of Mathematical Physics 51 (9): 093512. doi:10.1063/1.3490195. ISSN 0022-2488. Bibcode: 2010JMP....51i3512B.
- ↑ F. Pastawski; A. Kay; N. Schuch; J. I. Cirac (2010). "Limitations of passive protection of quantum information". Quantum Information and Computation 10 (7&8): 580. doi:10.26421/qic10.7-8. ISSN 1533-7146.
- ↑ Freeman, C. Daniel; Herdman, C. M.; Gorman, D. J.; Whaley, K. B. (7 October 2014). "Relaxation dynamics of the toric code in contact with a thermal reservoir: Finite-size scaling in a low-temperature regime". Physical Review B 90 (13): 134302. doi:10.1103/physrevb.90.134302. ISSN 1098-0121. Bibcode: 2014PhRvB..90m4302F.
- ↑ Hamma, Alioscia; Castelnovo, Claudio; Chamon, Claudio (18 June 2009). "Toric-boson model: Toward a topological quantum memory at finite temperature". Physical Review B 79 (24): 245122. doi:10.1103/physrevb.79.245122. ISSN 1098-0121. Bibcode: 2009PhRvB..79x5122H.
- ↑ Chesi, Stefano; Röthlisberger, Beat; Loss, Daniel (6 August 2010). "Self-correcting quantum memory in a thermal environment". Physical Review A 82 (2): 022305. doi:10.1103/physreva.82.022305. ISSN 1050-2947. Bibcode: 2010PhRvA..82b2305C.
- ↑ Pedrocchi, Fabio L.; Chesi, Stefano; Loss, Daniel (10 March 2011). "Quantum memory coupled to cavity modes". Physical Review B 83 (11): 115415. doi:10.1103/physrevb.83.115415. ISSN 1098-0121. Bibcode: 2011PhRvB..83k5415P.
- ↑ Alicki, R.; Horodecki, M.; Horodecki, P.; Horodecki, R. (2010). "On Thermal Stability of Topological Qubit in Kitaev's 4D Model". Open Systems & Information Dynamics 17 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1142/s1230161210000023. ISSN 1230-1612.
- ↑ Ghosh, Joydip; Fowler, Austin G.; Geller, Michael R. (19 December 2012). "Surface code with decoherence: An analysis of three superconducting architectures". Physical Review A 86 (6): 062318. doi:10.1103/physreva.86.062318. ISSN 1050-2947. Bibcode: 2012PhRvA..86f2318G.
- ↑ Bullock, Stephen S; Brennen, Gavin K (14 March 2007). "Qudit surface codes and gauge theory with finite cyclic groups". Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical 40 (13): 3481–3505. doi:10.1088/1751-8113/40/13/013. ISSN 1751-8113. Bibcode: 2007JPhA...40.3481B.
- ↑ Levin, Michael A. and Xiao-Gang Wen (12 January 2005). "String-net condensation: A physical mechanism for topological phases". Physical Review B 71 (45110): 21. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.71.045110. Bibcode: 2005PhRvB..71d5110L.
- ↑ Wootton, James R.; Lahtinen, Ville; Doucot, Benoit; Pachos, Jiannis K. (2011). "Engineering complex topological memories from simple Abelian models". Annals of Physics 326 (9): 2307–2314. doi:10.1016/j.aop.2011.05.008. ISSN 0003-4916. Bibcode: 2011AnPhy.326.2307W.
- ↑ Aguado, M.; Brennen, G. K.; Verstraete, F.; Cirac, J. I. (22 December 2008). "Creation, Manipulation, and Detection of Abelian and Non-Abelian Anyons in Optical Lattices". Physical Review Letters 101 (26): 260501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.101.260501. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 19113760. Bibcode: 2008PhRvL.101z0501A.
- ↑ Brennen, G K; Aguado, M; Cirac, J I (22 May 2009). "Simulations of quantum double models". New Journal of Physics 11 (5): 053009. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/11/5/053009. ISSN 1367-2630. Bibcode: 2009NJPh...11e3009B.
- ↑ Liu, Yu-Jie; Shtengel, Kirill; Smith, Adam; Pollmann, Frank (2022-11-07). "Methods for Simulating String-Net States and Anyons on a Digital Quantum Computer". PRX Quantum 3 (4): 040315. doi:10.1103/PRXQuantum.3.040315. Bibcode: 2022PRXQ....3d0315L. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PRXQuantum.3.040315.
- ↑ Pachos, J K; Wieczorek, W; Schmid, C; Kiesel, N; Pohlner, R; Weinfurter, H (12 August 2009). "Revealing anyonic features in a toric code quantum simulation". New Journal of Physics 11 (8): 083010. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/11/8/083010. ISSN 1367-2630. Bibcode: 2009NJPh...11h3010P.
- ↑ C.-Y. Lu, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 030502 (2009).
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 Satzinger, K. J.; Liu, Y.; Smith, A.; Knapp, C.; Newman, M.; Jones, C.; Chen, Z.; Quintana, C. et al. (2021-04-02). "Realizing topologically ordered states on a quantum processor". Science 374 (6572): 1237–1241. doi:10.1126/science.abi8378. PMID 34855491. Bibcode: 2021Sci...374.1237S.
- ↑ Yao, Xing-Can; Wang, Tian-Xiong; Chen, Hao-Ze; Gao, Wei-Bo; Fowler, Austin G.; Raussendorf, Robert; Chen, Zeng-Bing; Liu, Nai-Le et al. (22 February 2012). "Experimental demonstration of topological error correction". Nature 482 (7386): 489–494. doi:10.1038/nature10770. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 22358838. Bibcode: 2012Natur.482..489Y.
- ↑ Douçot, Benoit; Ioffe, Lev B.; Vidal, Julien (3 June 2004). "Discrete non-Abelian gauge theories in Josephson-junction arrays and quantum computation". Physical Review B 69 (21): 214501. doi:10.1103/physrevb.69.214501. ISSN 1098-0121. Bibcode: 2004PhRvB..69u4501D.
- ↑ Gladchenko, Sergey; Olaya, David; Dupont-Ferrier, Eva; Douçot, Benoit; Ioffe, Lev B.; Gershenson, Michael E. (2009). "Superconducting nanocircuits for topologically protected qubits". Nature Physics 5 (1): 48–53. doi:10.1038/nphys1151. ISSN 1745-2473. Bibcode: 2009NatPh...5...48G.
- ↑ Micheli, A.; Brennen, G. K.; Zoller, P. (30 April 2006). "A toolbox for lattice-spin models with polar molecules". Nature Physics 2 (5): 341–347. doi:10.1038/nphys287. ISSN 1745-2473. Bibcode: 2006NatPh...2..341M.
- ↑ Paredes, Belén; Bloch, Immanuel (1 January 2008). "Minimum instances of topological matter in an optical plaquette". Physical Review A 77 (2): 023603. doi:10.1103/physreva.77.023603. ISSN 1050-2947. Bibcode: 2008PhRvA..77b3603P.
- ↑ Dai, Hanning; Yang, Bing; Reingruber, Andreas; Sun, Hui; Xu, Xiao-Fan; Chen, Yu-Ao; Yuan, Zhen-Sheng; Pan, Jian-Wei (28 August 2017). "Four-body ring-exchange interactions and anyonic statistics within a minimal toric-code Hamiltonian". Nature Physics 13 (2): 1195–1200. doi:10.1038/NPHYS4243. ISSN 1745-2473. Bibcode: 2017NatPh..13.1195D.
- ↑ Weimer, Hendrik; Müller, Markus; Lesanovsky, Igor; Zoller, Peter; Büchler, Hans Peter (14 March 2010). "A Rydberg quantum simulator". Nature Physics 6 (5): 382–388. doi:10.1038/nphys1614. ISSN 1745-2473. Bibcode: 2010NatPh...6..382W.
- ↑ Semeghini, Giulia; Levine, Harry; Keesling, Alexander; Ebadi, Sepehr; Wang, Tout T.; Bluvstein, Dolev; Verresen, Ruben; Pichler, Hannes et al. (2021). "Probing Topological Spin Liquids on a Programmable Quantum Simulator". Science 374 (6572): 1242–1247. doi:10.1126/science.abi8794. PMID 34855494. Bibcode: 2021Sci...374.1242S.
- ↑ Bluvstein, Dolev; Levine, Harry; Semeghini, Giulia; Wang, Tout; Ebadi, Sepehr; Kalinowski, Marcin; Maskara, Nishad; Pichler, Hannes et al. (April 20, 2022). "A quantum processor based on coherent transport of entangled atom arrays". Nature 604 (7906): 451–456. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04592-6. PMID 35444318. Bibcode: 2022Natur.604..451B.
External links