Quantum complexity theory
This article includes a list of references, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient inline citations. (March 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Quantum complexity theory is the subfield of computational complexity theory that deals with complexity classes defined using quantum computers, a computational model based on quantum mechanics. It studies the hardness of computational problems in relation to these complexity classes, as well as the relationship between quantum complexity classes and classical (i.e., non-quantum) complexity classes.
Two important quantum complexity classes are BQP and QMA.
Background
A complexity class is a collection of computational problems that can be solved by a computational model under certain resource constraints. For instance, the complexity class P is defined as the set of problems solvable by a Turing machine in polynomial time. Similarly, quantum complexity classes may be defined using quantum models of computation, such as the quantum circuit model or the equivalent quantum Turing machine. One of the main aims of quantum complexity theory is to find out how these classes relate to classical complexity classes such as P, NP, BPP, and PSPACE.
One of the reasons quantum complexity theory is studied are the implications of quantum computing for the modern Church-Turing thesis. In short the modern Church-Turing thesis states that any computational model can be simulated in polynomial time with a probabilistic Turing machine.[1][2] However, questions around the Church-Turing thesis arise in the context of quantum computing. It is unclear whether the Church-Turing thesis holds for the quantum computation model. There is much evidence that the thesis does not hold. It may not be possible for a probabilistic Turing machine to simulate quantum computation models in polynomial time.[1]
Both quantum computational complexity of functions and classical computational complexity of functions are often expressed with asymptotic notation. Some common forms of asymptotic notion of functions are , , and . expresses that something is bounded above by where is a constant such that and is a function of , expresses that something is bounded below by where is a constant such that and is a function of , and expresses both and .[3] These notations also have their own names. is called Big O notation, is called Big Omega notation, and is called Big Theta notation.
Overview of complexity classes
The important complexity classes P, BPP, BQP, PP, and PSPACE can be compared based on promise problems. A promise problem is a decision problem which has an input assumed to be selected from the set of all possible input strings. A promise problem is a pair , where is the set of yes instances and is the set of no instances, and the intersection of these sets is empty: . All of the previous complexity classes contain promise problems.[4]
| Complexity Class | Criteria |
|---|---|
| P | Promise problems for which a polynomial time deterministic Turing machine accepts all strings in and rejects all strings in [4] |
| BPP | Promise problems for which a polynomial time Probabilistic Turing machine accepts every string in with a probability of at least , and accepts every string in with a probability of at most [4] |
| BQP | Promise problems such that for functions , there exists a polynomial time generated family of quantum circuits , where is a circuit which accepts qubits and gives an output of one qubit. An element of is accepted by with a probability greater than or equal to . An element of is accepted by with a probability less than or equal to .[4] |
| PP | Promise problems for which a polynomial time Probabilistic Turing machine accepts every string in with a probability greater than , and accepts every string in with a probability of at most [4] |
| PSPACE | Promise problems for which a deterministic Turing machine, that runs in polynomial space, accepts every string in and rejects all strings in [4] |
BQP
Answer produced Correct
answer |
Yes | No |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | ≥ 2/3 | ≤ 1/3 |
| No | ≤ 1/3 | ≥ 2/3 |
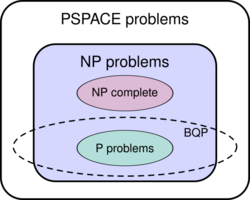
The class of problems that can be efficiently solved by a quantum computer with bounded error is called BQP ("bounded error, quantum, polynomial time"). More formally, BQP is the class of problems that can be solved by a polynomial-time quantum Turing machine with error probability of at most 1/3.
As a class of probabilistic problems, BQP is the quantum counterpart to BPP ("bounded error, probabilistic, polynomial time"), the class of problems that can be efficiently solved by probabilistic Turing machines with bounded error.[6] It is known that and widely suspected, but not proven, that , which intuitively would mean that quantum computers are more powerful than classical computers in terms of time complexity.[7] BQP is a subset of PP.
The exact relationship of BQP to P, NP, and PSPACE is not known. However, it is known that ; that is, the class of problems that can be efficiently solved by quantum computers includes all problems that can be efficiently solved by deterministic classical computers but does not include any problems that cannot be solved by classical computers with polynomial space resources. It is further suspected that BQP is a strict superset of P, meaning there are problems that are efficiently solvable by quantum computers that are not efficiently solvable by deterministic classical computers. For instance, integer factorization and the discrete logarithm problem are known to be in BQP and are suspected to be outside of P. On the relationship of BQP to NP, little is known beyond the fact that some NP problems are in BQP (integer factorization and the discrete logarithm problem are both in NP, for example). It is suspected that ; that is, it is believed that there are efficiently checkable problems that are not efficiently solvable by a quantum computer. As a direct consequence of this belief, it is also suspected that BQP is disjoint from the class of NP-complete problems (if any NP-complete problem were in BQP, then it follows from NP-hardness that all problems in NP are in BQP).[8]
The relationship of BQP to the essential classical complexity classes can be summarized as:
It is also known that BQP is contained in the complexity class (or more precisely in the associated class of decision problems ),[8] which is a subset of PSPACE.
Simulation of quantum circuits
There is no known way to efficiently simulate a quantum computational model with a classical computer. This means that a classical computer cannot simulate a quantum computational model in polynomial time. However, a quantum circuit of qubits with quantum gates can be simulated by a classical circuit with classical gates.[3] This number of classical gates is obtained by determining how many bit operations are necessary to simulate the quantum circuit. In order to do this, first the amplitudes associated with the qubits must be accounted for. Each of the states of the qubits can be described by a two-dimensional complex vector, or a state vector. These state vectors can also be described a linear combination of its component vectors with coefficients called amplitudes. These amplitudes are complex numbers which are normalized to one, meaning the sum of the squares of the absolute values of the amplitudes must be one.[3] The entries of the state vector are these amplitudes. The amplitudes, acting as coefficients in the linear combination description, each correspond to a non-zero component of the state vector. As an equation this is described as or using Dirac notation. The state of the entire qubit system can be described by a single state vector. This state vector describing the entire system is the tensor product of the state vectors describing the individual qubits in the system. The result of the tensor products of the qubits is a single state vector which has dimensions and entries that are the amplitudes associated with each basis state or component vector. Therefore, amplitudes must be accounted for with a dimensional complex vector which is the state vector for the qubit system.[9] In order to obtain an upper bound for the number of gates required to simulate a quantum circuit we need a sufficient upper bound for the amount data used to specify the information about each of the amplitudes. To do this bits of precision are sufficient for encoding each amplitude.[3] So it takes classical bits to account for the state vector of the qubit system. Next the application of the quantum gates on amplitudes must be accounted for. The quantum gates can be represented as sparse matrices.[3] So to account for the application of each of the quantum gates, the state vector must be multiplied by a sparse matrix for each of the quantum gates. Every time the state vector is multiplied by a sparse matrix, arithmetic operations must be performed.[3] Therefore, there are bit operations for every quantum gate applied to the state vector. So classical gate are needed to simulate qubit circuit with just one quantum gate. Therefore, classical gates are needed to simulate a quantum circuit of qubits with quantum gates.[3] While there is no known way to efficiently simulate a quantum computer with a classical computer, it is possible to efficiently simulate a classical computer with a quantum computer. This is evident from the fact that .[4]
Quantum query complexity
One major advantage of using a quantum computational system instead of a classical one, is that a quantum computer may be able to give a polynomial time algorithm for some problem for which no classical polynomial time algorithm exists, but more importantly, a quantum computer may significantly decrease the calculation time for a problem that a classical computer can already solve efficiently. Essentially, a quantum computer may be able to both determine how long it will take to solve a problem, while a classical computer may be unable to do so, and can also greatly improve the computational efficiency associated with the solution to a particular problem. Quantum query complexity refers to how complex, or how many queries to the graph associated with the solution of a particular problem, are required to solve the problem. Before we delve further into query complexity, let us consider some background regarding graphing solutions to particular problems, and the queries associated with these solutions.
Query models of directed graphs
One type of problem that quantum computing can make easier to solve are graph problems. If we are to consider the amount of queries to a graph that are required to solve a given problem, let us first consider the most common types of graphs, called directed graphs, that are associated with this type of computational modelling. In brief, directed graphs are graphs where all edges between vertices are unidirectional. Directed graphs are formally defined as the graph , where N is the set of vertices, or nodes, and E is the set of edges.[10]
Adjacency matrix model
When considering quantum computation of the solution to directed graph problems, there are two important query models to understand. First, there is the adjacency matrix model, where the graph of the solution is given by the adjacency matrix: , with , if and only if .[11]
Adjacency array model
Next, there is the slightly more complicated adjacency array model built on the idea of adjacency lists, where every vertex, , is associated with an array of neighboring vertices such that , for the out-degrees of vertices , where is the minimum value of the upper bound of this model, and returns the "" vertex adjacent to . Additionally, the adjacency array model satisfies the simple graph condition, , meaning that there is only one edge between any pair of vertices, and the number of edges is minimized throughout the entire model (see Spanning tree model for more background).[11]
Quantum query complexity of certain types of graph problems
Both of the above models can be used to determine the query complexity of particular types of graphing problems, including the connectivity, strong connectivity (a directed graph version of the connectivity model), minimum spanning tree, and single source shortest path models of graphs. An important caveat to consider is that the quantum complexity of a particular type of graphing problem can change based on the query model (namely either matrix or array) used to determine the solution. The following table showing the quantum query complexities of these types of graphing problems illustrates this point well.
| Problem | Matrix model | Array model |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum spanning tree | ||
| Connectivity | ||
| Strong connectivity | , | |
| Single source shortest path | , | , |
Notice the discrepancy between the quantum query complexities associated with a particular type of problem, depending on which query model was used to determine the complexity. For example, when the matrix model is used, the quantum complexity of the connectivity model in Big O notation is , but when the array model is used, the complexity is . Additionally, for brevity, we use the shorthand in certain cases, where .[11] The important implication here is that the efficiency of the algorithm used to solve a graphing problem is dependent on the type of query model used to model the graph.
Other types of quantum computational queries
In the query complexity model, the input can also be given as an oracle (black box). The algorithm gets information about the input only by querying the oracle. The algorithm starts in some fixed quantum state and the state evolves as it queries the oracle.
Similar to the case of graphing problems, the quantum query complexity of a black-box problem is the smallest number of queries to the oracle that are required in order to calculate the function. This makes the quantum query complexity a lower bound on the overall time complexity of a function.
Grover's algorithm
An example depicting the power of quantum computing is Grover's algorithm for searching unstructured databases. The algorithm's quantum query complexity is , a quadratic improvement over the best possible classical query complexity , which is a linear search. Grover's algorithm is asymptotically optimal; in fact, it uses at most a fraction more queries than the best possible algorithm.[12]
Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm
The Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm is a quantum algorithm designed to solve a toy problem with a smaller query complexity than is possible with a classical algorithm. The toy problem asks whether a function is constant or balanced, those being the only two possibilities.[2] The only way to evaluate the function is to consult a black box or oracle. A classical deterministic algorithm will have to check more than half of the possible inputs to be sure of whether or not the function is constant or balanced. With possible inputs, the query complexity of the most efficient classical deterministic algorithm is .[2] The Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm takes advantage of quantum parallelism to check all of the elements of the domain at once and only needs to query the oracle once, making its query complexity .[2]
Other theories of quantum physics
It has been speculated that further advances in physics could lead to even faster computers. For instance, it has been shown that a non-local, but non-signaling hidden variable quantum computer could implement a search of an N-item database in at most steps, a slight speedup over Grover's algorithm, which runs in steps. Note, however, that neither search method would allow quantum computers to solve NP-complete problems in polynomial time.[13] Theories of quantum gravity, such as M-theory and loop quantum gravity, may allow even faster computers to be built. However, defining computation in these theories is an open problem due to the problem of time; that is, within these physical theories there is currently no obvious way to describe what it means for an observer to submit input to a computer at one point in time and then receive output at a later point in time.[14][15]
See also
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Vazirani, Umesh V. (2002). "A survey of quantum complexity theory". Quantum Computation. Proceedings of Symposia in Applied Mathematics. 58. pp. 193–217. doi:10.1090/psapm/058/1922899. ISBN 9780821820841.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Nielsen, Michael A., 1974- (2010). Quantum computation and quantum information. Chuang, Isaac L., 1968- (10th anniversary ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-00217-3. OCLC 665137861.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Cleve, Richard (2000), "An Introduction to Quantum Complexity Theory", Quantum Computation and Quantum Information Theory (WORLD SCIENTIFIC): pp. 103–127, doi:10.1142/9789810248185_0004, ISBN 978-981-02-4117-9, Bibcode: 2000qcqi.book..103C, http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/9789810248185_0004, retrieved October 10, 2020
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Watrous, John (2008-04-21). "Quantum Computational Complexity". arXiv:0804.3401 [quant-ph].
- ↑ Nielsen, p. 42
- ↑ Nielsen, Michael; Chuang, Isaac (2000). Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-521-63503-5. OCLC 174527496. https://books.google.com/books?id=aai-P4V9GJ8C.
- ↑ Nielsen, p. 201
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Bernstein, Ethan; Vazirani, Umesh (1997). "Quantum Complexity Theory". SIAM Journal on Computing 26 (5): 1411–1473. doi:10.1137/S0097539796300921. http://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~vazirani/bv.ps.
- ↑ Häner, Thomas; Steiger, Damian S. (2017-11-12). "0.5 petabyte simulation of a 45-qubit quantum circuit". Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis. New York, NY, USA: ACM. pp. 1–10. doi:10.1145/3126908.3126947. ISBN 978-1-4503-5114-0. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/3126908.3126947.
- ↑ Nykamp, D.Q.. "Directed Graph Definition". https://mathinsight.org/definition/directed_graph.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Durr, Christoph; Heiligman, Mark; Hoyer, Peter; Mhalla, Mehdi (January 2006). "Quantum query complexity of some graph problems". SIAM Journal on Computing 35 (6): 1310–1328. doi:10.1137/050644719. ISSN 0097-5397.
- ↑ Zalka, Christof (1999-10-01). "Grover's quantum searching algorithm is optimal". Physical Review A 60 (4): 2746–2751. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.60.2746. Bibcode: 1999PhRvA..60.2746Z. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevA.60.2746.
- ↑ Aaronson, Scott (2005). "Quantum Computing and Hidden Variables". Phys. Rev. A 71 (3). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.71.032325. http://www.scottaaronson.com/papers/qchvpra.pdf.
- ↑ Aaronson, Scott (2005). "NP-complete Problems and Physical Reality". ACM SIGACT News 2005. Bibcode: 2005quant.ph..2072A. See section 7 "Quantum Gravity": "[...] to anyone who wants a test or benchmark for a favorite quantum gravity theory,[author's footnote: That is, one without all the bother of making numerical predictions and comparing them to observation] let me humbly propose the following: can you define Quantum Gravity Polynomial-Time? [...] until we can say what it means for a 'user' to specify an 'input' and 'later' receive an 'output'—there is no such thing as computation, not even theoretically." (emphasis in original)
- ↑ "D-Wave Systems sells its first Quantum Computing System to Lockheed Martin Corporation". D-Wave. 25 May 2011. http://www.dwavesys.com/en/pressreleases.html#lm_2011.
References
- Nielsen, Michael; Chuang, Isaac (2000). Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-63503-5. OCLC 174527496.
- Arora, Sanjeev; Barak, Boaz (2016). Computational Complexity: A Modern Approach. Cambridge University Press. pp. 201–236. ISBN 978-0-521-42426-4. https://archive.org/details/computationalcom00aror.
- Watrous, John (2008). "Quantum Computational Complexity". arXiv:0804.3401v1 [quant-ph].
- Watrous J. (2009) Quantum Computational Complexity. In: Meyers R. (eds) Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science. Springer, New York, NY
External links
 |