Astronomy:BH Virginis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Right ascension | 13h 58m 24.860s[2] |
| Declination | −01° 39′ 38.95″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.60 - 10.56[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Main sequence |
| Spectral type | G0 V + G2 V[4] |
| B−V color index | 0.650±0.043[5] |
| Variable type | Algol + RS CVn[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −22.80±2.7[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 2.672[2] mas/yr Dec.: −5.742[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 6.6834 ± 0.0181[2] mas |
| Distance | 488 ± 1 ly (149.6 ± 0.4 pc) |
| Orbit[4] | |
| Period (P) | 0.8169 d |
| Semi-major axis (a) | ≥1.55 Gm (2.23 R☉) |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.0 |
| Inclination (i) | 87.5±0.8[7]° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,431,241.389±1.0 JD |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 0.0° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 137.8 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 135.2 km/s |
| Details | |
| Component 1 | |
| Mass | 1.173±0.006[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.22±0.05[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2.19[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.30[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 5,969±11[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.1[8] dex |
| Component 2 | |
| Mass | 1.046±0.005[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.11±0.04[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.20[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.35[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 5,500[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.3[8] dex |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
BH Virginis is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. With a typical apparent visual magnitude of 9.6,[3] it is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of approximately 488 light years from the Sun.[2] The system is drifting closer with a net radial velocity of −23 km/s.[6]
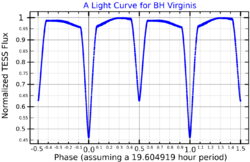
This system was determined to be a short period variable star by C. Hoffmeister in 1935.[11] W. Zessewitsch found a period of 19.6 hours for the system in 1944. In 1957, M. Kitamura and associates refined the light curve of this Algol-type eclipsing variable and discovered some irregular fluctuations not explained by the eclipse cycle.[12] R. H. Koch in 1967 reported observing a change in the depth of the primary eclipse.[13] In 1982, M. Hoffmann concluded that both stars are intrinsically variable, indicating this is an RS Canum Venaticorum variable system.[14]
This is a near-contact[15] binary system with a circular orbit having a period of 19.61 hours.[4] The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 88° to the line of sight from the Earth,[7] allowing both components to eclipse each other once per orbit. During the deep[4] primary eclipse the system decreases in brightness by 0.96 magnitude, while the shallower secondary eclipse decreases the system by 0.64 magnitude.[15] Cyclical oscillations in the orbital period have been observed with two short-term periods of 9.2 and 11.8 years, and a longer-term oscillation of 51.7 years. The short term oscillations may be due to magnetic activity on the stars, while the longer period could be caused by an unseen third body.[16]
Both components of this system are G-type main-sequence stars, with stellar classifications of G0V and G2V, respectively.[4] Evidence of star spots have been found on both stars, but appear to be predominantly on the secondary component.[9] The two stars are somewhat larger and more massive than the Sun.[7]
References
- ↑ MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes, Space Telescope Science Institute, https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html, retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, 5.1 61 (1): 80–88, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Abt, Helmut A. (October 1965), "Spectrographic Measures of the Eclipsing System BH Virginis", Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 77 (458): 367, doi:10.1086/128233, Bibcode: 1965PASP...77..367A.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331–346, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Karataș, Yüksel et al. (2004), "Kinematics of chromospherically active binaries and evidence of an orbital period decrease in binary evolution", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 349 (3): 1069–1092, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07588.x, Bibcode: 2004MNRAS.349.1069K.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 Kjurkchieva, D. P. et al. (September 2004), "Spectroscopic and photometric observations of the short-period RS CVn-type star BH Virginis", Astronomy and Astrophysics 424 (3): 993–1002, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20035902, Bibcode: 2004A&A...424..993K.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Clement, R. et al. (September 1997), "Absolute parameters for binary systems. I. The active binary BH Virginis", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 124 (3): 499–508, doi:10.1051/aas:1997367, Bibcode: 1997A&AS..124..499C.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Xiang, Fuyuan et al. (October 2007), "Evidence of Hot Spot Activity on BH Virginis", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 59 (5): 955–960, doi:10.1093/pasj/59.5.955, Bibcode: 2007PASJ...59..955X.
- ↑ "BH Vir". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=BH+Vir.
- ↑ Hoffmeister, Cuno (June 1935), "162 neue Veräderliche", Astronomische Nachrichten 255 (22): 401, doi:10.1002/asna.19352552202, Bibcode: 1935AN....255..401H. Listed as "– 0 2769" then "HD 121909" in a footnote.
- ↑ Kitamura, M. et al. (1957), "A Photoelectric Study of the Eclipsing System BH Virginis", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 9: 191, Bibcode: 1957PASJ....9..191K.
- ↑ Koch, Robert H. (April 1967), "The complicated eclipsing binary, BH Virginis", Astronomical Journal 72: 411, doi:10.1086/110243, Bibcode: 1967AJ.....72..411K.
- ↑ Hoffmann, M. (March 1982), "The variable light curve of BH Vir", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 47: 561–568, Bibcode: 1982A&AS...47..561H.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Avvakumova, E. A. et al. (October 2013), "Eclipsing variables: Catalogue and classification", Astronomische Nachrichten 334 (8): 860, doi:10.1002/asna.201311942, Bibcode: 2013AN....334..860A.
- ↑ Tian, Yong-Po et al. (June 2008), "On the Period Variations of BH Virginis", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 60 (3): 571–575, doi:10.1093/pasj/60.3.571, Bibcode: 2008PASJ...60..571T.
Further reading
- Kozhevnikova, A. V. et al. (November 2007), "Long-term starspot activity of the eclipsing binaries BH Vir and WY Cnc", Astronomy Reports 51 (11): 932–946, doi:10.1134/S1063772907110066, Bibcode: 2007ARep...51..932K.
- Xiang, Fu Yuan; Zhou, Yi Chun (June 2004), "A Photometric Analysis and Spot Activity of BH Virginis", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 56 (3): 469–474, doi:10.1093/pasj/56.3.469, Bibcode: 2004PASJ...56..469X.
- Xiang, F. Y.; Zhou, Y. C. (January 2004), "The spot activity of BH Virginis", New Astronomy 9 (1): 27–31, doi:10.1016/j.newast.2003.07.001, Bibcode: 2004NewA....9...27X.
- Arevalo, M. J. et al. (January 2002), "J and K Infrared Light Curves of the Active Binary BH Vir", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 5222: 1, Bibcode: 2002IBVS.5222....1A.
- Xiang, F. Y. et al. (October 2000), "Star-spots activity on BH Virginis", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 146: 7–12, doi:10.1051/aas:2000260, Bibcode: 2000A&AS..146....7X.
- Qian, Shengbang et al. (2000), "Orbital Period Studies of RS CVn-type binaries III. BH Virginis", Astrophysics and Space Science 274 (4): 859–866, doi:10.1023/A:1026512806446, Bibcode: 2000Ap&SS.274..859Q.
- Popper, Daniel M. (September 1997), "Orbits of detached main-sequence eclipsing binaries of types late F to K. II. UV leonis, UV piscium, and BH virginis", The Astronomical Journal 114: 1195, doi:10.1086/118552, Bibcode: 1997AJ....114.1195P.
- Xiang, F. Y.; Liu, Q. Y. (August 1997), "The variable light curve of BH Virginis", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 124 (2): 281–282, doi:10.1051/aas:1997191, Bibcode: 1997A&AS..124..281X.
- Lazaro, C.; Arevalo, M. J. (June 1997), "Time-Resolved Spectroscopy of RS CVn Short-Period Systems. I. CG CYG, BH VIR, and ER VUL", Astronomical Journal 113: 2283, doi:10.1086/118439, Bibcode: 1997AJ....113.2283L.
- Clement, R. et al. (May 1997), "Four colour photometry of late-type binary systems. II. New light curves of BH Virginis", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 123: 59–61, doi:10.1051/aas:1997343, Bibcode: 1997A&AS..123...59C.
- Heckert, P. A.; Summers, D. L. (August 1995), "1994 photometry of BH Virginis", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 4225: 1, Bibcode: 1995IBVS.4225....1H.
- Heckert, P. A.; Summers, D. L. (August 1994), "1993 BVRI Photometry of BH Virginis", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 4062: 1, Bibcode: 1994IBVS.4062....1H.
- Zhai, D. S. et al. (October 1990), "An analysis of basic parameters and SPOT activities of the solar-type binary system BH Virginis", Astronomy and Astrophysics 237: 148, Bibcode: 1990A&A...237..148Z.
- Arévalo, M. J.; Lázaro, C. (July 1990), "The Photometric Behaviour of BH Vir", Astrophysics and Space Science 169 (1–2): 245–246, doi:10.1007/BF00640724, Bibcode: 1990Ap&SS.169..245A.
- Derman, E. et al. (December 1989), "1989 Light Curves of BH Vir", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3404: 1, Bibcode: 1989IBVS.3404....1D.
- Zeilik, M. et al. (May 1990), "Long-Term Starspot Activity of Short-Period RS Canum Venaticorum Stars. III. BH Virginis", Astrophysical Journal 354: 352, doi:10.1086/168693, Bibcode: 1990ApJ...354..352Z.
- Arevalo, M. J. et al. (December 1987), "1986 BV Light Curves of BH Virginis", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3117: 1, Bibcode: 1987IBVS.3117....1A.
- Scaltriti, F. et al. (August 1985), "Photometry of southern stars. II. Further evidence of spots in the eclipsing binary BH Virginis", Astronomy and Astrophysics 149: 11–14, Bibcode: 1985A&A...149...11S.
- Giuricin, G. et al. (January 1984), "Lightcurve analysis for the eclipsing binaries ST Car, RY Ind and BH Vir", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 206 (2): 305–313, doi:10.1093/mnras/206.2.305, Bibcode: 1984MNRAS.206..305G.
- Botsula, R. A. (1978), "Instability in detached binary systems of the main sequence with solar-type components. II. BH Virginis" (in Russian), Peremennye Zvezdy 20: 577–587, Bibcode: 1978PZ.....20..577B.
- Whitney, B. S. (1955), "Minima and periods of eclipsing stars", Astronomical Journal 60: 453, doi:10.1086/107258, Bibcode: 1955AJ.....60..453W.
 |