Chemistry:Silver tetrafluoroborate
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Silver tetrafluoridoborate(1–)
| |
| Other names
Borate(1-), tetrafluoro-, silver(1+)
Argentous tetrafluoroborate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AgBF4 | |
| Molar mass | 194.673 g/mol |
| Appearance | Off-white powder |
| Odor | almost odorless |
| Density | 4.16 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 71.5 °C (160.7 °F; 344.6 K) (monohydrate) |
| soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
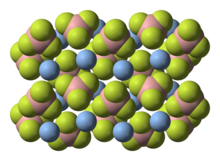
Silver tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgBF4. It is a white solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents as well as water. In its solid state, the Ag+ centers are bound to fluoride.[2]
Preparation
Silver tetrafluoroborate is prepared by the reaction between boron trifluoride and silver oxide in the presence of benzene.
Laboratory uses
In the inorganic and organometallic chemistry laboratory, silver tetrafluoroborate, sometimes referred to "silver BF-4", is a useful reagent. In dichloromethane, silver tetrafluoroborate is a moderately strong oxidant.[3] Similar to silver hexafluorophosphate, it is commonly used to replace halide anions or ligands with the weakly coordinating tetrafluoroborate anions. The abstraction of the halide is driven by the precipitation of the appropriate silver halide.
References
- ↑ "Silver tetrafluoroborate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/159722#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Evgeny Goreshnik, Zoran Mazej, "X-ray single crystal structure and vibrational spectra of AgBF4" Solid State Sciences 2005, Volume 7, pp. 1225–1229. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2005.06.007
- ↑ N. G. Connelly, W. E. Geiger (1996). "Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic Chemistry". Chemical Reviews 96 (2): 877–910. doi:10.1021/cr940053x. PMID 11848774.
 |


