Chemistry:Ozenoxacin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | oz en ox' a sin |
| Trade names | Ozanex; Xepi |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a618010 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
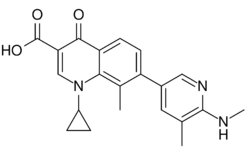
| Formula | C21H21N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 363.417 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ozenoxacin, sold under the brand names Ozanex and Xepi, is a quinolone antibiotic used for the treatment of impetigo.[3] A 1% topical cream is approved for treatment of impetigo in Canada[4] and in the United States.[5][6]
Ozenoxacin is active against some bacteria that have developed resistance to fluoroquinolone antibiotics.[7]
Mechanism of Action
Like other quinolone antibiotics, ozenoxacin targets DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.[8]
Its activity against bacteria with fluoroquinolone resistance is attributed to its evasion of bacterial efflux pumps.[7]
Chemistry
Synthesis

Ozenoxacin is synthesized by the Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling of a bromoquinolone and a pyridyl tributylstannane (Stille coupling).[9][10]
The pyridyl tributylstannane is synthesized from the corresponding dihalopyridine. This is achieved through a sequence of nucleophilic aromatic substitution with methylamine, which is protected as the acetamide using acetic anhydride and this is converted to the organostannane through a Pd-catalyzed stannylation with bis(tributyltin).
The bromoquinolone is made from the N-cyclopropyl aniline and diethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate, which react through a Michael addition, followed by elimination of the ethoxy group and then a Friedel-Crafts acylation at elevated temperature. The N-cyclopropyl aniline is prepared by a Pd-catalyzed cross coupling of 2,6-dibromotoluene and cyclopropylamine (Buchwald-Hartwig coupling).
References
- ↑ "Xepi- ozenoxacin cream". 30 January 2020. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=2765b37b-4862-473f-b4cd-8da908088e8b.
- ↑ https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/psusa/ozenoxacin-list-nationally-authorised-medicinal-products-psusa/00010651/202205_en.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ↑ "Ozenoxacin" (in en). PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/9863827.
- ↑ "Cipher Pharmaceuticals Receives Health Canada Approval of Ozanex (ozenoxacin cream 1%)" (Press release). Cipher Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- ↑ "Medimetriks Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Receives FDA Approval for Xepi (ozenoxacin) Cream, 1%, a Novel Topical Antibiotic for Impetigo" (Press release). Medimetriks Pharmaceuticals, Inc. – via PRNewswire.
- ↑ "Xepi (ozenoxacin) Cream". 18 January 2018. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2017/208945Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "In vitro activity of Ozenoxacin against quinolone-susceptible and quinolone-resistant gram-positive bacteria". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (12): 6389–6392. December 2013. doi:10.1128/AAC.01509-13. PMID 24080666.
- ↑ "Ozenoxacin: a review of preclinical and clinical efficacy". Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy 17 (3): 159–168. March 2019. doi:10.1080/14787210.2019.1573671. PMID 30686133.
- ↑ Hayashi K, Kito T, Mitsuyama J, Yamakawa T, Kuroda H, Kawafuchi H, "Quinolonecarboxylic acid derivatives or salts thereof", US patent 6335447, issued 2002-01-01, assigned to Toyama Chemical Co Ltd
- ↑ "Synthetic Approaches to the New Drugs Approved During 2015". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 60 (15): 6480–6515. August 2017. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00010. PMID 28421763.
External links
- "Ozenoxacin". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/ozenoxacin.
 |
