Fluent (mathematics)
From HandWiki
| Part of a series of articles about |
| Calculus |
|---|
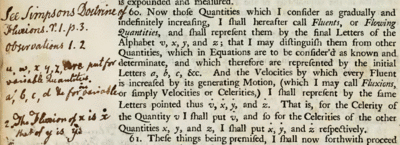
A fluent is a time-varying quantity or variable.[1] The term was used by Isaac Newton in his early calculus to describe his form of a function.[2] The concept was introduced by Newton in 1665 and detailed in his mathematical treatise, Method of Fluxions.[3] Newton described any variable that changed its value as a fluent – for example, the velocity of a ball thrown in the air. The derivative of a fluent is known as a fluxion, the main focus of Newton's calculus. A fluent can be found from its corresponding fluxion through integration.[4]
See also
- Method of Fluxions
- History of calculus
- Leibniz–Newton calculus controversy
- Derivative
- Newton's notation
- Fluxion
References
- ↑ Newton, Sir Isaac (1736) (in en). The Method of Fluxions and Infinite Series: With Its Application to the Geometry of Curve-lines. Henry Woodfall; and sold by John Nourse. https://books.google.com/books?id=WyQOAAAAQAAJ. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
- ↑ Fluent (mathematics) at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Fluent". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Fluent.html.
- ↑ "Isaac Newton (1642-1727)". http://www.mhhe.com/math/calc/smithminton2e/cd/tools/timeline/newton.html. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
 |
