Chemistry:Himbacine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
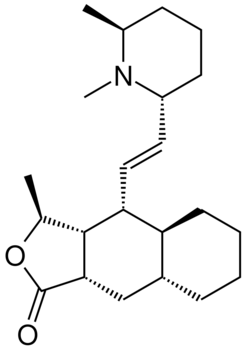 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H35NO2 |
| Molar mass | 345.527 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Himbacine is an alkaloid isolated from the bark of Australian magnolias. Himbacine has been synthesized using a Diels-Alder reaction as a key step.[1] Himbacine's activity as a muscarinic receptor antagonist, with specificity for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2, made it a promising starting point in Alzheimer's disease research.[2][3] The development of a muscarinic antagonist based on himbacine failed but an analog, vorapaxar, has been approved by the FDA as a thrombin receptor antagonist.[4][5]
References
- ↑ "Total Synthesis of (+)-Himbacine and (+)-Himbeline". J. Org. Chem. 64 (6): 1932–1940. March 1999. doi:10.1021/jo981983+. PMID 11674285.
- ↑ "Chemical Modification of Ring C of Himbacine: Discovery of a Pharmacophoric Element for M2-Selectivity". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 5 (1): 61–66. 1995. doi:10.1016/0960-894X(94)00459-S.
- ↑ "Himbacine analogs as muscarinic receptor antagonists-effects of tether and heterocyclic variations". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 14 (15): 3967–3970. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.05.047. PMID 15225708.
- ↑ "Discovery of a Novel, Orally Active Himbacine-Based Thrombin Receptor Antagonist (SCH 530348) with Potent Antiplatelet Activity". J. Med. Chem. 51 (11): 3061–3064. 2008. doi:10.1021/jm800180e. PMID 18447380.
- ↑ "Blog entry about Himbacine and its history in drug development". 13 May 2008. http://blogs.sciencemag.org/pipeline/in_which_i_hate_a_wonder_drug.
 |

