Astronomy:Wolf 424
Coordinates: ![]() 12h 33m 17.38s, +09° 01′ 15.8″
12h 33m 17.38s, +09° 01′ 15.8″
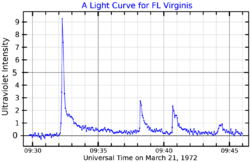 An ultraviolet band light curve for FL Virginis, adapted from Moffett (1972).[1] The plot shows intensity above the star's quiescent intensity. | |
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Right ascension | 12h 33m 17.38s[2] |
| Declination | +09° 01′ 15.8″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | A: 13.22 ± 0.01 B: 13.21 ± 0.01[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | dM6e/dM6e[4] |
| U−B color index | 1.19/ |
| B−V color index | 1.84/ |
| Variable type | Flare stars |
| Astrometry | |
| Wolf 424 A | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −2[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −1710.468±0.554[6] mas/yr Dec.: 203.098±0.451[6] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 223.4775 ± 0.4665[6] mas |
| Distance | 14.59 ± 0.03 ly (4.475 ± 0.009 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 15.03[7] |
| Wolf 424 B | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −1795.661±0.565[8] mas/yr Dec.: 217.789±0.550[8] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 231.1185 ± 0.5119[8] mas |
| Distance | 14.11 ± 0.03 ly (4.327 ± 0.010 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 15.02[7] |
| Orbit[3] | |
| Primary | GJ 473 A |
| Companion | GJ 473 B |
| Period (P) | 15.532 ± 0.096 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 0.9257 ± 0.0049" (4.062 ± 0.098 AU) |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.2950 ± 0.0035 |
| Inclination (i) | 103.00 ± 0.15° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 143.48 ± 0.19° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 1992.297 ± 0.056 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 347.2 ± 1.5° |
| Details | |
| Mass | A: 0.143 ± 0.011 B: 0.131 ± 0.010[3] M☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| ARICNS | A |
| B | |
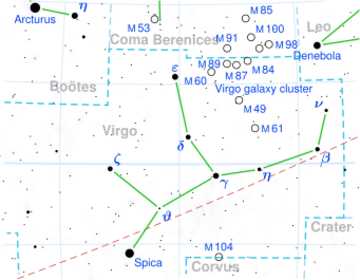
Location of Wolf 424 in the constellation Virgo | |
Wolf 424 is a binary star system comprising two red dwarf stars at a distance of approximately 14.2 light years from the Sun. It is located in the constellation Virgo, between the stars ε Virginis and ο Virginis.
The close binary nature of this star was discovered by Dutch American astronomer Dirk Reuyl in 1941, based upon an elongation of the star found in photographs.[3] The two stars in the Wolf 424 system orbit about each other with a semi-major axis of 4.1 AU and an eccentricity of 0.3. The stars have an orbital period of 15.5 years and have a combined apparent magnitude of about 12.5.
Wolf 424A is a cool main sequence red dwarf star of approximately 0.14 solar masses (147 Jupiters) and a radius of 0.17 solar radii. Its companion, Wolf 424B, is a cool main sequence red dwarf star of approximately 0.13 solar masses (136 Jupiters) and a radius of 0.14 solar radii. They are two of the dimmest known objects within 15 light years of the Sun. In 1967, it was discovered that both are flare stars that undergo random increases in luminosity. The system has been designated FL Virginis, and may experience sunspot activity. The stars may undergo variation in the level of flare activity over periods lasting several years.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Moffett, T. J. (January 1973). "Wolf 424: a neglected flare star". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 164: 11–20. doi:10.1093/mnras/164.1.11. Bibcode: 1973MNRAS.164...11M.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cutri, Roc M.; Skrutskie, Michael F.; Van Dyk, Schuyler D.; Beichman, Charles A.; Carpenter, John M.; Chester, Thomas; Cambresy, Laurent; Evans, Tracey E. et al. (2003). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: 2MASS All-Sky Catalog of Point Sources (Cutri+ 2003)". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 2246: II/246. Bibcode: 2003yCat.2246....0C. http://vizier.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR?-source=II/246.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Torres, Guillermo (January 1999). "The Nearby Low-Mass Visual Binary Wolf 424". The Astronomical Journal 117 (1): 562–573. doi:10.1086/300708. Bibcode: 1999AJ....117..562T.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Pettersen, B. R. (May 2006). "Flare variability in the close binary FL Vir". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 368 (3): 1392–1394. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10210.x. Bibcode: 2006MNRAS.368.1392P.
- ↑ Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953). "General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities". Carnegie Institute Washington D.C. Publication (Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington). Bibcode: 1953GCRV..C......0W.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Staff (January 1, 2010). "List of the Nearest 100 Stellar Systems". Research Consortium on Nearby Stars. http://www.recons.org/TOP100.posted.htm.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- W. D. Heintz, "Astrometric study of 4 binary stars", 1972, Astronomical Journal, 77, 160.
- Cohen, E. Richard; David R. Lide; George L. Trigg (2003). AIP Physics Desk Reference. Birkhäuser. pp. 100. ISBN 0-387-98973-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=JStYf6WlXpgC&pg=PA100.
External links
- Wolf 424 Data page
- Wolf 424 AB
- A NASA image of Wolf 424 AB
- "V* FL Vir". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=V%2A+FL+Vir.
 |