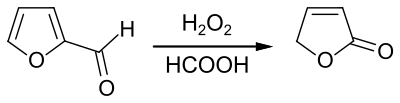Chemistry:2-Furanone
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Furan-2(5H)-one | |||
| Other names
Furan-2-one, γ-crotonolactone, butenolide, 5H-furan-2-one
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 383585 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 773828 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | butenolide | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 84.07336 | ||
| Density | 1.185 g/cm3, liquid | ||
| Melting point | 4 to 5 °C (39 to 41 °F; 277 to 278 K)[1] | ||
| Boiling point | 86 to 87 °C (187 to 189 °F; 359 to 360 K) 12 mm Hg[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
2-Furanone is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is also known as γ-crotonolactone (GCL), as it is formally the lactone derived from γ-hydroxyisocrotonic acid. The chemical is colloquially called "butenolide", and is the parent structure for the butenolide class of compounds. It is a colourless liquid.
Synthesis and reactions
2-Furanone is prepared by oxidation of furfural:[2]
It exists in equilibrium with the tautomer 2-hydroxyfuran, which serves as an intermediate in the interconversion between the β- and α-furanones.[further explanation needed] The β form is the more stable. The interconversion is catalyzed by base.
2-Furanones can be converted to furans by a two-step process of reduction followed by dehydration.
See also
- Category:Furanones, various substituted structural analogs
- Pyrone, which has one more carbon atom in the ring
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals Product detail
- ↑ Näsman, Jan H. (1990). "3-Methyl-2(5H)-furanone". Organic Syntheses 68: 162. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.068.0162.
 |